Kinematical Equations for Circular Motion
Kinematical Equations for Circular Motion: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Kinematics of Circular Motion etc.
Important Questions on Kinematical Equations for Circular Motion
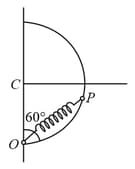
A smooth semicircular wire track of radius is fixed in a vertical plane. One end of a massless spring of natural length is attached to the lowest point of the wire track. A small ring of mass which can slide on the track is attached to the other end of the spring. The ring is held stationary at point such that the spring makes an angle of with the vertical. The spring constant . Consider the instant when the ring is released. The normal reaction on the ring by the track is
Starting form rest, a particle rotates in a circle of radius m with an angular acceleration α = π/4 rad/s2. The magnitude of average velocity of the particle over the time it rotates quarter circle is
A cyclist riding the bicycle at a speed of takes a turn around a circular road of radius without skidding. Given , what is his inclination to the vertical.
The angular velocity of the minute hand of a clock is :
To enable a particle to describe circular motion the angle between its velocity and acceleration is given by
Which one is the correct relation between the magnitude of linear acceleration and angular acceleration in circular motion of radius of circular path.
Assume is linear acceleration and is angular acceleration.
Write the kinematical equations for circular motion in analogy with linear motion.
A rod is moving on a fixed circle of radius with constant velocity , as shown in the figure. is the point of intersection of the rod and the circle. At an instant, the rod is at a distance from the centre of the circle. The velocity of the rod is perpendicular to the rod and the rod is always parallel to the diameter .
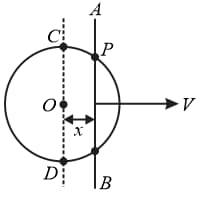
(a) Find the speed of point of intersection .
(b) Find the angular speed of point of intersection with respect to centre of the circle.
Cotyledons are also called-
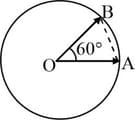
Two particles and are moving on circle. At a certain instant of time both the particles are diametrically opposite and P has tangential acceleration and centripetal acceleration whereas has only centripetal acceleration of . At that instant acceleration (in ) of with respect to is
Three identical cars A, B and C are moving at the same speed on three bridges. The car A goes on a plane bridge, B on a bridge convex upwards and C goes on a bridge concave upwards. Let and be the normal forces exerted by the cars on the bridges when they are at the middle of the bridges. Then
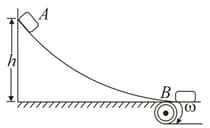
Particles are released from rest at A and slide down the smooth surface of height h to a conveyor B. The correct angular velocity of the conveyor pulley of radius r to prevent any sliding on the belt as the particles transfer to the conveyor is
A wheel having radius 10 cm is coupled by a belt to another wheel of radius 30cm. 1st wheel increases its angular speed from rest at a uniform rate of 1.57 . The time for 2nd wheel to reach a rotational speed of 100 rev/min is...(assume that the belt does not slip)
A stationary wheel starts rotating about its own axis at constant angular acceleration. If the wheel completes 50 rotations in first 2 seconds, then the number of rotations made by it in next two seconds is
A stationary wheel starts rotating about its own axis at uniform angular acceleration . The time taken by it to complete rotations is
When a ceiling fan is switched off, its angular velocity reduces to while it makes rotations. How many more rotations will it make before coming to rest? (Assume uniform angular retardation)
If is angular acceleration, is angular velocity and is the centripetal acceleration then, which of the following is true?
Consider the following controls in an automobile: gas pedal, brake, steering wheel. The controls in this list that cause an acceleration of the car are -
A cyclist starts from the centre of a circular track of radius , reaches the edge of the track and then cycles along the circumference and stops at point as shown in the figure. If the total time taken is , what is the average velocity of the cyclist ?
A hollow vertical cylinder of radius and height has smooth internal surface. A small particle is placed in contact with the inner side of the upper rim at a point . It is given a horizontal speed tangential to rim. It leaves the lower rim at point , vertically below . The number of revolutions made by the particle will be -
