Angular Impulse
Angular Impulse: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Angular Impulse, Angular Impulse with Constant Torque, Angular Impulse with Time Varying Torque, Angular Impulse with Torque and Time Graph & Angular Momentum from Angular Impulse etc.
Important Questions on Angular Impulse
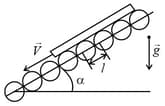
A homogeneous plank of mass and length is released gently on an inclined rolling mill, which consists of a large number of uniform horizontal cylindrical rollers. Axes of the roller are fixed parallel to each other in a plane inclined at an angle with the horizontal with a separation
between two adjacent axes. The mass of a roller is , each roller can rotate about its axis without friction and acceleration due to gravity is . Long time after the plank is released; it acquires a steady speed . If this steady speed is , then find .
A constant torque acting on a uniform circular wheel changes its angular momentum from to in . The magnitude of this torque is
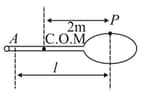
In a mess fighting match between Bheema and Duryodhana, Bheema swings his mess to hit the target with a constant angular velocity After hitting target mess comes to rest and surprisingly bheema feels no impulsive reaction on his hand. Mess hits the target at point as shown in figure. If Bheema holds the mess at end then will be. Given: Moment of inertia of mess about is Total mass is
A uniform rod of mass and length lying on a smooth horizontal table is pivoted about one end. An impulse is applied to the other end. Angular speed with which rod starts rotating is
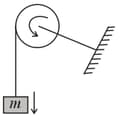
A mass is suspended through a thread wrapped around a disc-shaped pulley of mass as shown in the figure. Friction in the axle of the pulley is absent and there is no slipping of thread. When the mass falls through a vertical distance 2 metre, the velocity acquired by it, is
A thin uniform rod of length and mass suspended vertically is free to rotate about a smooth horizontal axis which passes through its end . point mass moving horizontally with velocity hits the lower end of the rod and sticks to it. After collision the rod just reaches the horizontal position. Which of the following statements is WRONG?
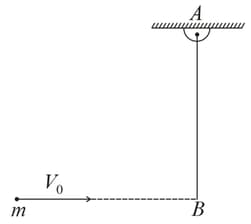
A solid sphere of radius rests on a horizontal surface. A horizontal impulse is applied on sphere at height from centre, as shown in figure below. The sphere starts rolling just after the application of impulse. What will be the ratio ?
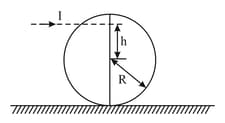
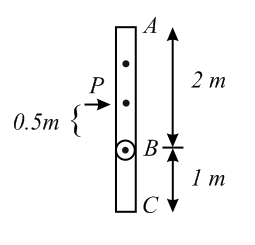
Two uniform rods and of masses and respectively having lengths and respectively are joined to each other at . They can rotate freely about without any friction. The assembly is kept on a smooth horizontal surface as shown in the figure. A horizontal impulse is applied on the rod at a distance from point perpendicular to the rod.
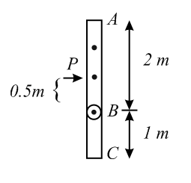
Two uniform rods and of masses and respectively having lengths and respectively are joined to each other at . They can rotate freely about without any friction. The assembly is kept on a smooth horizontal surface as shown in the figure. A horizontal impulse is applied on the rod at a distance from point perpendicular to the rod.
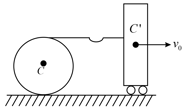
A smooth uniform disc of mass and radius is connected with a heavy cart by an inextensible string. When the cart is pushed with a velocity ,
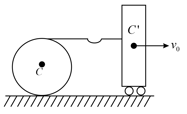
A smooth uniform disc of mass and radius is connected with a heavy cart by an inextensible string. When the cart is pushed with a velocity ,
A uniform rod of mass and Length at rest on a smooth horizontal surface. An impulse of force is applied to end B. The time taken by the rod to turn through at right angles will be where ____.
A uniform solid sphere of mass and radius is placed on a smooth horizontal surface. It is given a horizontal impulse at a height above the centre of mass and sphere starts rolling. Then the value of and speed of centre of mass are
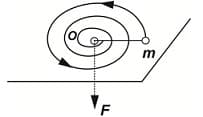
A small body of mass m tied to a non-stretchable thread moves over a smooth horizontal plane. The other end of the thread is being drawn into a hole O (fig) with a constant velocity. The dependence of the thread tension on the distance r between the body and the hole if at the angular velocity of the thread is equal to will be
The figure here shows a uniform rod of mass m and length at rest, in a gravity free region. The rod is hinged at one of its ends. The rod is oriented along y - axis, in the position shown here.
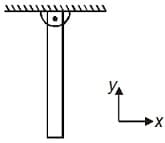
Suppose that the rod is made of charged non - conducting material. The linear charge density on the rod varies with distance from the hinge as here is a constant and n is real number. The rod is in rest position and now a uniform electric field is suddenly switched on in the region for an instant. Value of n, for which there is no reaction at the hinge, is
A uniform rod AB of mass m and length is at rest on a smooth horizontal surface. An impulse p is applied to the end B. The time taken by the rod to turn through a right angle is
A uniform rod of mass and length rests on a smooth table and is free to turn about a smooth pivot at its end , in contact with it at a distance from is an inelastic particle of mass , a horizontal blow of impulse is given to the rod at a distance from in a direction perpendicular to the rod. The resultant instantaneous angular velocity of the rod is
A uniform rod of mass , length rests on a smooth horizontal surface. Rod is given a sharp horizontal impulse perpendicular to the rod at a distance from the centre. The angular velocity of the rod will be
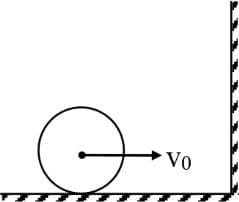
A cylinder is rolling over frictionless horizontal surface with velocity as shown in figure. Coefficient of friction between wall and cylinder is . If the collision between cylinder and wall is completely inelastic, then kinetic energy of cylinder after collision -
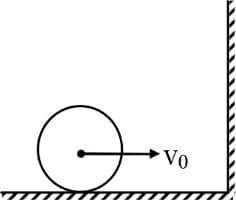
A cylinder is rolling over frictionless horizontal surface with velocity as shown in figure. Coefficient of friction between wall and cylinder is . If the collision between cylinder and wall is completely inelastic, then kinetic energy of cylinder after collision -