Dynamics of Rigid Bodies with Fixed Axis of Rotation
Dynamics of Rigid Bodies with Fixed Axis of Rotation: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Angular Impulse, Angular Impulse with Constant Torque, Angular Impulse with Time Varying Torque, Angular Impulse with Torque and Time Graph & Angular Momentum from Angular Impulse etc.
Important Questions on Dynamics of Rigid Bodies with Fixed Axis of Rotation
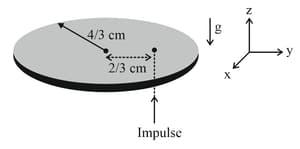
A thin circular coin of mass and radius is initially in a horizontal -plane. The coin is tossed vertically up ( direction) by applying an impulse of at a distance from its center. The coin spins about its diameter and moves along the direction. By the time the coin reaches back to its initial position, it completes rotations. The value of is _____.
[Given: The acceleration due to gravity ]
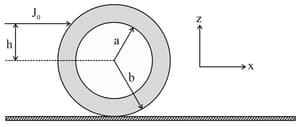
An annular disk of mass , inner radius and outer radius is placed on a horizontal surface with coefficient of friction , as shown in the figure. At some time, an impulse is applied at a height above the center of the disk. If then the disk rolls without slipping along the -axis. Which of the following statement(s) is(are) correct?
A uniform square plate of mass and edge initially at rest starts rotating about one of the edge under the action of a constant torque . Then at the end of the after start
Find the angular velocity of a body rotating with an acceleration of as it completes the revolution after the start.
A body rotates about a fixed axis with an angular acceleration of . Through what angle does it rotate during the time in which its angular velocity increases from to ?
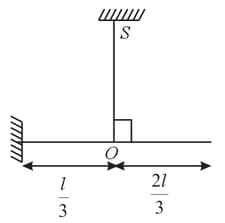
A rod of mass and length is suspended from a vertical wall and kept horizontal by a massless vertical thread as shown. The tension in the thread is,
A body is in pure rolling motion on a horizontal surface. For which body the rotational kinetic energy is not less than translational kinetic energy
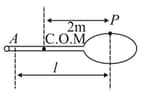
In a mess fighting match between Bheema and Duryodhana, Bheema swings his mess to hit the target with a constant angular velocity After hitting target mess comes to rest and surprisingly bheema feels no impulsive reaction on his hand. Mess hits the target at point as shown in figure. If Bheema holds the mess at end then will be. Given: Moment of inertia of mess about is Total mass is
If a perfectly inelastic peg located at distance a vertically below stops the lamina bringing it to instantaneous rest. then the impulsive reaction at the moment of impact is
If a ceiling fan is switched off,its angular velocity falls to half after it makes 36 rotations.Then Find the number of rotations it will make before coming to rest?
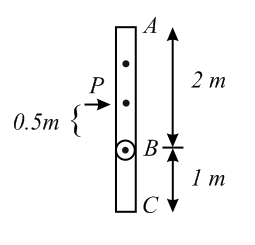
Two uniform rods and of masses and respectively having lengths and respectively are joined to each other at . They can rotate freely about without any friction. The assembly is kept on a smooth horizontal surface as shown in the figure. A horizontal impulse is applied on the rod at a distance from point perpendicular to the rod.
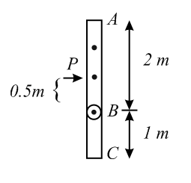
Two uniform rods and of masses and respectively having lengths and respectively are joined to each other at . They can rotate freely about without any friction. The assembly is kept on a smooth horizontal surface as shown in the figure. A horizontal impulse is applied on the rod at a distance from point perpendicular to the rod.
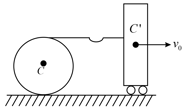
A smooth uniform disc of mass and radius is connected with a heavy cart by an inextensible string. When the cart is pushed with a velocity ,
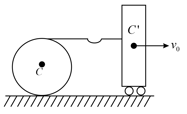
A smooth uniform disc of mass and radius is connected with a heavy cart by an inextensible string. When the cart is pushed with a velocity ,
A frictionless hinge supports a bar of mass m and length L in the vertical position. The hinge is a sort of pivot that can offer no resistance to the bar against an applied moment. However, the reaction is what it offers. If the bar is released, find the reaction at the support, when the bar comes down to the horizontal position.
A uniform rod of length is fixed at one end. It is initially held vertically upward, then released. Find the vertical reaction at hinge when it becomes horizontal.
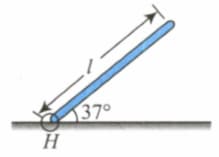
A uniform rod of mass and length can rotate in vertical plane about a smooth horizontal axis hinged at point . It is released from initial position making an angle of with horizontal. Find force (in ) exerted by the hinge just after the rod is released from rest.
A solid sphere is rotating about a diameter with uniform angular speed. Which of the following options is/are correct?
The figure here shows a uniform rod of mass m and length at rest, in a gravity free region. The rod is hinged at one of its ends. The rod is oriented along y - axis, in the position shown here.
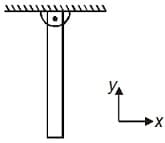
Suppose that the rod is made of charged non - conducting material. The linear charge density on the rod varies with distance from the hinge as here is a constant and n is real number. The rod is in rest position and now a uniform electric field is suddenly switched on in the region for an instant. Value of n, for which there is no reaction at the hinge, is
A uniform rod AB of mass m and length is at rest on a smooth horizontal surface. An impulse p is applied to the end B. The time taken by the rod to turn through a right angle is
