Angular Momentum in Case of Rotation about a Fixed Axis
Angular Momentum in Case of Rotation about a Fixed Axis: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Angular Momentum of a Rigid Body in Pure Rotation, Angular Momentum and Angular Velocity, and Conservation of Angular Momentum in Pure Rotation.
Important Questions on Angular Momentum in Case of Rotation about a Fixed Axis
A man stand on a rotating platform with his arms stretched is holding a weight in each hand. The angular speed of the platform is . The moment of inertia of the man together with the platform may be taken to be constant and equal to . If the man brings his arms close to his chest with the distance of each weight from the axis changing from to , the new angular speed of the platform is
Two bodies have moments of inertia and respectively about their axis of rotation. If their kinetic energies of rotation are equal, their angular momenta will be in the ratio of
A solid cylinder of mass and radius rotates about its axis with an angular speed . The angular momentum of the cylinder about its axis is
An ice skater spins at with her arms extended. If her moment of inertia with arms folded is of that with arms extended, her angular velocity when she folds her arms is
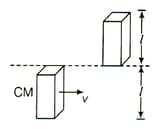
A bar of mass m length l is in pure translatory motion with its centre of mass velocity v. It collides with and sticks to another identical bar at rest as shown in figure. Assuming that after collision it becomes one composite bar of length 2l. The angular velocity of the composite bar will be.