Center of Mass
Center of Mass: Overview
This topic describes the centre of mass of a system and its significance. It also contains mathematical expressions to prove the centre of mass with the example of rod and lamina.
Important Questions on Center of Mass
For a bangle, the centre of mass lie outside the body.
For which of the following does the centre of mass lie outside the body ?
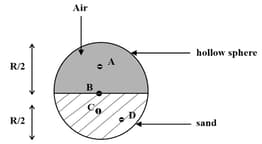
The centre of mass of solid hemisphere of radius is from the centre of the flat surface. Then value of is _________ .
Give an example to show that the following statement is false. 'Any two forces acting on a body can be combined into single force that would have same effect'.
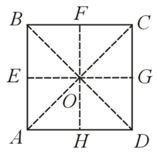
For the given uniform square lamina ABCD whose centre is O, pick incorrect statement :-
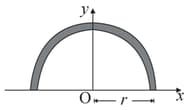
The coordinate of centre of mass of a thin and uniform semicircular ring of radius shown in figure is
Centre of mass of a uniform ring is at the _____ of the ring.
(Choose from: circumference/centre)
Consider a two-particle system with particles having masses and . If the first particle is pushed towards the centre of mass through a distance , by what distance should the second particle be moved, so as to keep the centre of mass at the same position?
Which of the following points is the likely position of the centre of mass of the system shown in figure?
Two particles each of mass are placed at a distance of and respectively from the origin along -axis. The centre of the mass of the system of the particles is
Two particles each of mass are placed at a distance of and respectively from the origin along -axis. The centre of the mass of the system of the particles is
Centre of mass of a uniform ring is at the _____ of the ring.
Two particles and , initially at rest, move towards each other under a mutual force of attraction. At the instant when the speed of is and the speed of is , the speed of the center of mass of the system is:
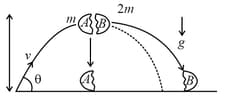
A projectile is launched from the origin with speed at an angle from the horizon. At the highest point in the trajectory, the projectile breaks into two pieces, and of masses and respectively. Immediately after the breakup, piece is at rest relative to the ground. Neglect air resistance. Which of the following sentences most accurately describes what happens next?
In a molecule, the separation between the nuclei of the two atoms is about . Given that a chlorine atom is about times as massive as a hydrogen atom and nearly all the mass of an atom is concentrated in its nucleus, the position of centre of mass of the molecule is
Center of mass of three particles of masses and lies at the point and center of mass of another system of particles and lies at the point . The point at which a particle of mass be placed, so that the center of mass of first system coincides with centre of mass of whole system is:
The center of mass of a system of two particles of masses and is at a distance from and at a distance from mass , such that:
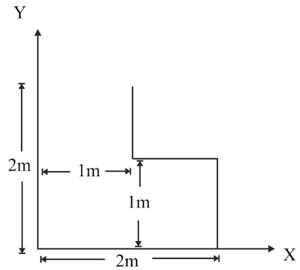
The coordinates of the center of mass of a uniform shaped lamina of mass is:
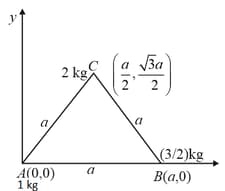
Three particles of masses and are located at the vertices of an equilateral triangle (see figure below). The coordinates of centre of mass of this system is located at:
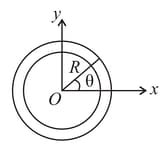
Find the coordinates of the centre of mass of the non-uniform circular ring of radius R given below. Take the origin to be at the centre of the circle. Let be the angle that the radius vector through any element or the ring makes with the -axis. The density of the circular ring as a function of is given as (where is a constant)