Motion of Center of Mass
Motion of Center of Mass: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Velocity of Centre of Mass, Acceleration of Centre of Mass & Explosion of a Projectile in Its Path etc.
Important Questions on Motion of Center of Mass
Two blocks of masses are connected by a spring of negligible mass and placed on a frictionless horizontal surface. An impulse gives a velocity of to the block in the direction of other block. The velocity (in ) of the centre of mass is:-
In case of an isolated system, the centre of mass of the system moves with a constant _____.
A small ball is moving inside a box which is placed on a smooth horizontal surface. During motion, the ball makes collisions with the walls of the box then the position of the centre of mass:
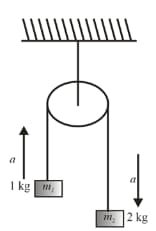
Two masses and are connected by a light inextensible string and suspended by means of a weightless pulley as shown in the figure. Assuming that both the masses start from rest, the distance travelled by center of mass in two seconds is (Take )
Two particles of equal mass have velocities and . First particle has an acceleration while the acceleration of the other particle is zero. The centre of mass of the two particles moves in a path of
Two blocks of masses and are connected by a spring of negligible mass and placed on a frictionless horizontal surface. An impulse gives a velocity of to the heavier block in the direction of the lighter block. The velocity of the centre of mass in is , then
A solid sphere of mass M and radius 2R rolls down an inclined plane of height without slipping. The speed of its centre of mass when it reaches the bottom is
A bomb of mass 1 kg is thrown vertically upwards with a speed of . After 5 seconds it explodes into two fragments. One fragment of mass 400 gm is found to go down with a speed of . What will happen to the second fragment just after the explosion?
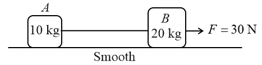
Two blocks A and B are connected by a massless string (shown in fig.) A force of 30 N is applied on block B. Find the distance travelled by centre of mass in 2 seconds starting from rest
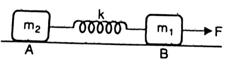
Two bodies A and B of masses and respectively are connected by a massless spring of force constant k. A constant force F starts acting on the body A at . Then
A solid cylinder of mass m and radius R rolls down an inclined plane of height h without slipping. The speed of its centre of mass when it reaches the bottom is
A thin rod of length L is vertically straight on horizontal floor. This rod falls freely to one side without slipping of its bottom. The linear velocity of centre of rod when its top end touches floor is
A man of mass stands at one end of a plank of length which lies at rest on a frictionless surface. The man walks to the other end of the plank. If the mass of the plank is , the distance that the man moves relative to the ground is -
A man weighing is standing in a trolley weighing . The trolley is resting on frictionless horizontal rails. If the man starts walking on the trolley with a speed of , then after , his displacement relative to the ground will be -
Two blocks of masses and respectively are tied to the ends of a string which passes over a light frictionless pulley. The masses are held at rest at the same horizontal level and then released. The distance traversed by centre of mass in is -
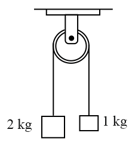
The two bodies of mass and respectively are tied to the ends of a massless string, which passes over a light and frictionless pulley. The masses are initially at rest and then released. Then acceleration of the centre of mass of the system is
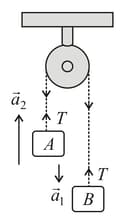
Find the velocity of centre of the system shown in the figure.
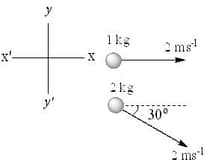
The motion of the centre of mass is the result of:
A body of mass while falling vertically downwards under gravity breaks into two parts: a body of mass and a body of mass . The centre of mass of bodies and taken together shift compared to that of the body towards:
Two practical and initially at rest, move towards each other under mutual force of attraction. At an instance when the speed of is and speed is , the speed of centre of mass () is:
