Potential Energy
Potential Energy: Overview
In this topic, we will learn the concepts of potential energy of an object. We will also derive its formula by taking the example of gravitational potential energy and work done by a conservative force.
Important Questions on Potential Energy
If potential energy function for the force between two atoms in a diatomic molecule is approximately given by , where and are constants in standard SI units and is in metres. Find the dissociation energy of the molecule (in ). [Take and ]
Which of the following is true for an Unstable equilibrium ?
For unstable equilibrium,the second derivative should be Negative.
A rectangle block rests on a horizontal table. A horizontal force is applied on the block at a height above the table to move the block. Does the line of action of the normal force exerted by the table on the block depend on ?
For equilibrium, the net moment acting on the body by various forces is zero.
The energy of a body due to its position or change in shape is known as _____energy.
Formula for potential energy is_____.
A body is falling from a height h. After it has fallen a height h/2, it will possess_____.
Water stored in a dam possesses_____.
A car is accelerated on a levelled road and attains a velocity 4 times of its initial velocity. In this process the potential energy of the car_____.
The energy possessed by a body due to its position is called
If mass of an object, m = 10 kg, displacement (height) h = 6m, and acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.8 ms-2. Then potential energy is
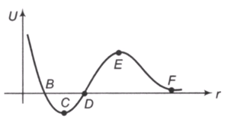
The given plot shows the variation of , the potential energy of interaction between two particles with the distance separating them .
1. and are equilibrium points
2. is a point of stable equilibrium
3. The force of interaction between the two particles is attractive between points and and repulsive between and
4. The force of interaction between particles is repulsive between points and .
Which of the above statements is correct?
represents the potential energy between two atoms in a molecule, where is the distance between the atoms and and are positive. The atom will be in stable equilibrium if
A particle of mass lying on axis experiences a force given by law, , where is the coordinate of the particle in .
In the arrangements shown below, all the balls are identical and strings are light. There is no friction. In each of the three arrangements and , the system is in equilibrium.
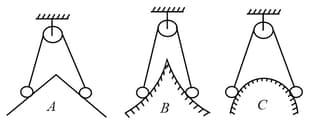
The hill slopes are identical on the two slides in each of the arrangements.
One of the balls in each arrangement is pulled down a little along the hill slope.
If potential energy function for the force between two atoms in a diatomic molecule is approximately given by , where and are constants in standard SI units and is in metres. Find the dissociation energy of the molecule (in ). [Take and ]
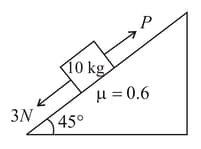
A block of mass is kept on a rough inclined plane as shown in the figure. The coefficient of friction between the block and the surface is . Two forces of magnitude and P Newton are acting on the block. If friction on the block is acting upwards then minimum value of P for which the block remains at rest is:
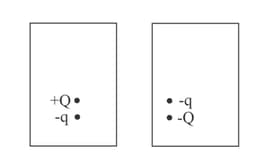
In the following diagrams, a particle with small charge - q is free to move up or down, but not sideways near a larger fixed charge Q. The small charge is in equilibrium because in the positions shown, the electrical upward force is equal to the weight of the particle. Which statement is true?