Conservative Forces and Potential Energy
Conservative Forces and Potential Energy: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Potential Energy, Force and Potential Energy, Calculation of Conservative Force from Potential Energy & Energy Stored in Spring etc.
Important Questions on Conservative Forces and Potential Energy
A uniform chain of length is kept on a table such that a length of hangs freely from the edge of the table. The total mass of the chain is . What is the work done in pulling the entire chain in the table?
A particle is moved from to under a force from two paths. Path is and path is . Let and be the work done by this force in these two paths. Then,
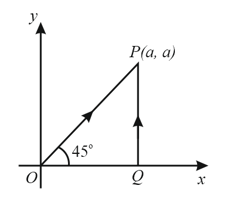
If and represent the work done in moving a particle from to along three different paths and , respectively (as shown), in the gravitational field of a point mass , find the correct relation between and .
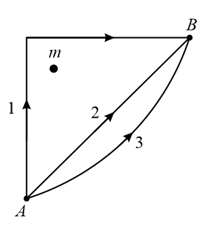
Which of the following forces is not conservative?
The of a particle of mass moving along the - axis is given by, , where is in . It can be concluded that the wrong option is
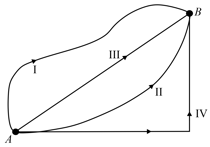
In a gravitational force field a particle is taken from to along different paths as shown in figure. Then
Assertion: Friction is a conservative force.
Reason: Friction does not depend upon mass of the body.
Frictional force is_______________.
Which of the following statement is not true?
The potential energy of a system increases if work is done
The potential energy of a particle is determined by the expression , where is a positive constant. The particle begins to move from a point with coordinates , only under the action of the potential field force. Then its kinetic energy at the instant when the particle is at a point with the coordinates is
The potential energy of a particle under a conservative force is given by . The equilibrium position of the particle is at:
The potential energy of a particle of mass moving in the plane is given by , where and are given in metre. If the particle starts from rest, from the origin, then the speed of the particle at is
Example of a non-conservative force is:
A spring long is stretched by the application of a force. If force required to stretch the spring through , then work done in stretching the spring through is
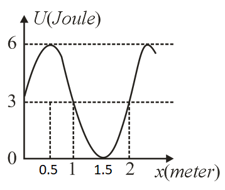
Potential energy curve (sinusoidal) is shown graphically for a particle. The potential energy does not depend on and coordinates. The maximum value of corresponding conservative force (in magnitude) for range is (in Newton). Find the value of .
When a block moves with some friction on ground,
The spring constant of the spring of a gun is newton/meter. The spring has been compressed meter from its normal position and a bullet of mass has been put in the barrel. If the friction is negligible then on firing the gun, the bullet shall have a velocity of
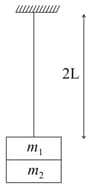
From a fixed support , hangs an elastic string of negligible mass and natural length . Masses and attached at the lower end, elongate the string to . When is removed gently, is able to bounce back to . The ratio is (assume that the string does not obstruct the motion of )
Calculate the force associated with the following one-dimensional potential energy :-
