Moseley’s Law
Moseley’s Law: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Different Series in Characteristic X-rays, Wavelength and Energy of Emitted X-ray Photons, Identifying Elements from X-ray Spectrum, Bragg's Diffraction & Moseley's Law in Characteristic X-rays etc.
Important Questions on Moseley’s Law
The element which has a -rays line of wavelength is and
If (nical) is used as target material, then is minimum wavelength produced in -ray tube and is the wavelength of line. If the operating tube voltage is increased and (calsium) is used as target material in place of then the difference will :
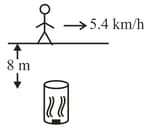
A student is jogging on a straight path with the speed per hour. Perpendicular to the path is kept a pipe with its opening from the road (see figure). Diameter of the pipe is At the other end of the pipe is a speaker emitting sound of towards the opening of the pipes. As the student passes in front of the pipe, she hears the speaker sound for seconds. is in the range (take speed of sound, ):
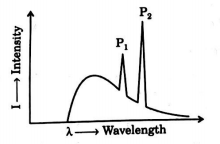
The wavelength of line from an element of atomic number is . From another element the wavelength of line is . What is the atomic number of second element?
For X-ray diffraction, order of size of obstacle is:
If the operating voltage of X-ray tube is then velocity of X-ray :-
In E.M. waves spectrum rays region lies between
Absorption of ray is maximum in which of the following sheets?
The wavelength of the -rays produced by an -ray tube is . What will be the atomic number of anode material?
For characteristic -ray of some material, which of the following must be true?
The -rays arising from a cobalt target have a wavelength of Which of the following is true about the -rays arising from a nickel target ?
The -ray wavelength of line of platinum is known to be . What is the -ray wavelength of line of molybdenum ?
Find the atomic number for an atom that emits radiation with wavelength , if wavelength emitted by an atom of atomic number .
Which of the following plots will give a straight line, when a metal of atomic number is used to target a Coolidge tube. Let be the frequency of the line. Given that corresponding values of and are known for a number of metals.
What will be the critical angle for a medium at air interface if the angle of polarisation is :-
Wavelengths associated with photon and electron are and , then correct statement will be:
The properties of X-ray as put forward by Rontgen in his pioneering paper on the topic are as follows:
1. X-ray posses a very strong penetrative power. It can penetrate wood upto $3 \mathrm{cm}$ and an aluminium foil upto $15 \mathrm{mm} .$ If the hand is held between the discharge tube and the screen the dark shadow of the bones is visible within the slightly dark shadow of the hand.
2. Photographic plates and films "show themselves susceptible to X-rays." Hence, photography provides a valuable method of studying the effects of X-rays.
3. X-rays are neither reflected nor refracted (so far as Rontgen could discover). Hence, "X-rays cannot be concentrated by lenses."
4. X-rays discharge electrified bodies, whether the electrification is positive or negative.
5. X-rays are generated when the cathode rays of the discharge tube strike any solid body. A heavier element, such a's platinum, however, is much more efficient as a generator of X-rays than a lighter element, such as aluminium,
Most of Rontgen's observations stood the test of time, though some of them needed to be modified later. Now today we know if electron are accelerated through a potential difference $V,$ then maximum energy of emitted photon could be
$E_{\max }=e V$
$\frac{h c}{\lambda_{\min }}=e V$
$\lambda_{\min }=\frac{h c}{e V}$
$\lambda_{\min }$ is also called cut off wavelength. Since electron may loose very small energy in a given collision, the upper value of $\lambda$ will approach infinity. When $\mathbf{X}$ -ray is produced in an X-ray tube, two types of X-ray spectra are observed : continuous spectra and line spectra.
A continuous spectrum is produced by bremsstrahlung, the electromagnetic radiation produced when free electrons are accelerated during collisions with ions. A line spectrum results when an electron having sufficient energy collides with a heavy atom, and an electron in an inner energy level is ejected from the atom. An electron from an outer energy level then fills the vacant inner energy level, resulting in emission of an X-ray photon.
The electron knocks out an inner shell electron of the atom with which it collides. Let us take a hypothetical case of a target atom whose $K$ -shell electron has been knocked out as shown.
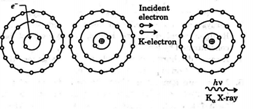
This will create a vacancy in $K$ -shell. Sensing this vacancy an electron from a higher energy state may make a transition to this vacant state. When such a transition takes place the difference of energy is converted into photon of electromagnetic radiation, which is called characteristic X-rays. Now depending upon the shell from which an electron makes a transition to $K$ -shell we may have different lines in the $K$ series of X-rays e.g., if electron from $L$ shell jumps to $K$ shell we have $K_{\alpha},$ if electron from $M$ shell jumps to $K$ shell we have $K_{\beta}$ X-ray and so on. Moseley conducted many experiments on characteristic X-rays, the findings of which played an important role in developing the concept of atomic number. Moseley's observations can be expressed as
$\sqrt{v}=a(Z-b)$
where $a$ and $b$ are constants. $Z$ is the atomic number of target atom and $n$ is the frequency.
Use the data given in the table shown to arrange the elements in the modern periodic table:
| Element | Wavelength | Atomic Weight |
| P | 1.94 Å | 55.8 |
| Q | 1.79 Å | 58.9 |
| R | 1.66 Å | 58.7 |
wavelength emitted by an atom, of atomic number is . Find the atomic number for an atom that emits radiation with wavelength .
