Radioactivity
Radioactivity: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Radioactivity, Natural Radioactivity, Artificial Radioactivity, Parent Nuclei, Daughter Nuclei, Displacement Law in Radioactivity, Radioactive Decay Law, Decay Constant, Mean Life of Radioactive Nucleus, etc.
Important Questions on Radioactivity
Two nuclei have mass numbers in the ratio . The ratio of their nuclear radii would be:
How long will a radioactive isotope, whose half life is years, take for its activity to reduce to of its initial value?
Two nuclei have mass numbers in the ratio . The ratio of their nuclear radii is:
The expression for the average life of a radionuclide that shows its relationship with the half – life would be:
In decay, the terms half-life period and decay constant is used. The relationship between the two is
A radioactive sample contains of pure which has half-life period of . Calculate the number of atoms present initially and the activity when of the sample will be left.
A radioactive sample contains of pure which has a half-life period of seconds. Calculate the number of atoms present initially, and the activity when of the sample will be left.
The radioactive decay rate of a radioactive element is found to be 103 disintegration/second at a certain time. If the half life of the elements is one second, the decay rate after one second is ________________ and after three seconds is _____________.
Two nuclei and have equal number of atoms at . Their half lives are hours and hours respectively. Their ratios of rates of disintegration after hours from the start is
The half life of polonium is days. In what time will of polonium be disintegrated out of its initial mass of
After two hours, one sixteenth of the starting amount of a certain radioactive isotope remained undecayed. The half life of isotope is
A radioactive element with a half life of hours decays giving a stable element . After a time t, the ratio of to atoms is , then time is
In a sample of radioactive material, what percentage of initial number of active nuclei will decay during one mean life?
When radioactive nucleus emits particle its atomic number and mass number are respectively
When radioactive nucleus emits an particle then dauter nucleus reduces in atomic number and mass number by
From the given plot of the decay rate versus time of some radioactive nuclei, the half life of the nuclei in hours can be estimated to be
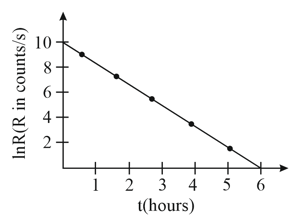
What is the probability that a radioactive nucleus will not have decayed after a time equal to twice its half-life?
A radioactive isotope has half-life of years. After how much time is its activity reduced to of its original activity? (Answer in years)
In a radioactive decay chain, the initial nucleus is . At the end, there are -particles and -particles which are emitted. If the end nucleus is and are given by:
