Electric Flux
Important Questions on Electric Flux
A point charge of is placed at the center of a sphere of radius . If , then the electric flux through the surface of the sphere will be
A charged particle is placed at the centre of cube of length . Another same charge is placed at a distance from . Then the electric flux through is
In a region of space, the electric field is given by The electric flux through a surface area of units in plane is,
Electric field is given by . Electric flux through surfaces of area layer in plane, plane and plane are in ratio
The electric field in a certain region is acting radially outward and is given by . A charge contained in a sphere of radius centred at the origin of the field, will be given by
A cylinder of radius and length is placed in a uniform electric field parallel to the cylinder axis. The total flux from the top and bottom faces of the cylinder is
The S.I. unit of electric flux is
The scalar product of electric field intensity and area vector through which the line of force emerges is ___________.
If , then the electric flux through a surface area of lying in the plane is (in ),
In a region of space having a spherically symmetric distribution of charge, the electric flux enclosed by a concentric spherical Gaussian surface varies with a radius as
where and are the constants.
The electric field strength in the region is given as,
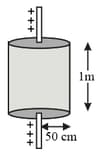
Electric charge is uniformly distributed along a long straight wire of radius . The charge per length of the wire is coulomb. Another cylindrical surface of radius and length symmetrically encloses the wire as shown in the figure. The total electric flux passing through the cylindrical surface is,
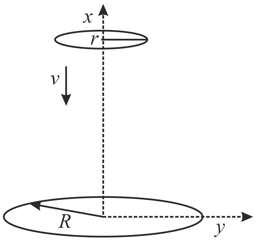
A ring of radius is placed in the plane with its centre at origin and its axis along the axis and having uniformly distributed positive charge. A ring of radius and coaxial with the larger ring is moving along the axis with constant velocity. Then, the variation of electric flux passing through the smaller ring with position will be best represented by,
A point charge is placed near a hemispherical surface without base, cylindrical surface with one end open, spherical surface, and hemispherical surface with the base as shown in the figures in and respectively. In which of the following cases, the flux crossing through the surface is zero?
A cylinder of radius and length is placed in a uniform electric field parallel to the cylinder axis. The total flux for the surface of the cylinder is given by
What will be the value of flux passing through surface S due to the given charge distribution?
Consider two concentric spherical surfaces with radius and with radius , both centred at the origin. There is a charge at the origin and there are no other charges. Compare the flux , through with the flux , through .
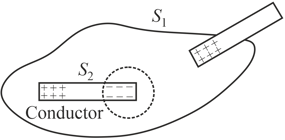
Charge on an originally uncharged conductor is separated by holding a positively charged rod very closely nearby, as shown in the figure. Assume that the induced negative charge on the conductor is equal to the positive charge on the rod. Then the flux through the surface is
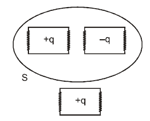
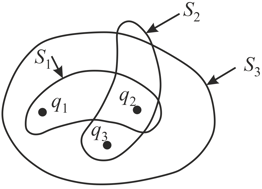
Three charges , and have been placed as shown in the figure. Then the net electric flux will be maximum for the surface
If the flux of the electric field through a closed surface is zero, then
Under what conditions can the electric flux be found through a closed surface?

