Electric Potential and Potential Difference
Important Questions on Electric Potential and Potential Difference
Considering a group of positive charges, which of the following statements is correct?
Which of the following correctly represents the variation of electric potential of a charged spherical conductor of radius with radial distance from the centre?
For a charged spherical ball, electrostatic potential inside the ball varies with as .
Here, and are constant and is the distance from the center. The volume charge density inside the ball is . The value of is ______.
permittivity of medium.
A point charge is moved from to in a uniform electric field of directed along positive -axis. If coordinates of and are respectively, the work done by electric field will be
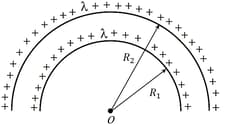
The electric potential at the centre of two concentric half rings of radii and , having same linear charge density is
identical drops are charged at each. They combine to form a bigger drop. The potential of the bigger drop will be _____ .
If the electric potential at any point in space is given by volt. The electric field at the point will be :
The two thin coaxial rings, each of radius and having charges and respectively are separated by a distance of . The potential difference between the centres of the two rings is :
In the given figure, a battery of emf is connected across a conductor of length and different area of cross-sections having radii and
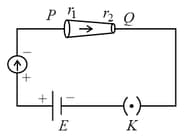
Choose the correct option as one moves from to .
identical drops of mercury are charged to a potential of each. The drops are joined to form a single drop. The potential of this drop is in Volt.
Ten charges are placed on the circumference of a circle of radius with constant angular separation between successive charges. Alternate charges have charge each, while have charge each. The potential V and the electric field E at the centre of the circle are respectively : (Take at infinity)
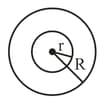
Concentric metallic hollow spheres of radii and hold charges and respectively. Given that surface charge density of the concentric spheres are equal, the potential difference is:
A charge Q is distributed over two concentric conducting thin spherical shells radii and . If the surface charge densities on the two shells are equal, the electric potential at the common centre is :
Consider two charged metallic spheres and of radii and respectively. The electric fields (on ) and (on ) on their surfaces are such that Then the ratio (on ) (on ) of the electrostatic potentials on each sphere is:
A uniformly charged ring of radius and total charge is placed in plane centred at origin. A point charge is moving towards the ring along the axis and has speed at . The minimum value of such that it crosses the origin is:
A solid conducting sphere, having a charge is surrounded by an uncharged conducting hollow spherical shell. Let the potential difference between the surface of the solid sphere and that of the outer surface of the hollow shell be If the shell is now given a charge of the new potential difference between the same two surfaces is:
The electric field in a region is given by where is in and is in metres. The values of constants are unit and unit. If the potential at is and that at is then is
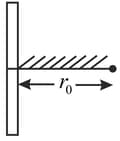
A positive point charge is released from rest at a distance from a positive line charge with uniform charge density. The speed of the point charge, as a function of instantaneous distance from line charge, is proportional to
A charge is distributed over three concentric spherical shells of radii such that their surface charge densities are equal to one another.
The total potential at a point at distance from their common centre, where would be:
There is a uniform electrostatic field in a region. The potential at various points on a small sphere centred at , in the region, is found to vary between the limits to . What is the potential at a point on the sphere whose radius vector makes an angle of with the direction of the field?

