Acceleration Due to Gravity
Important Questions on Acceleration Due to Gravity
The radius of the earth is about and that of the mars is . The mass of the earth is about times mass of the mars. An object weighs on the surface of the earth. Its weight on the surface of the mars will be
If the earth stops rotating suddenly, the value of at a place other than poles would:
Mars has a diameter of approximately of that of earth and mass of of that of earth. The surface gravitational field strength on mars as compared to that on earth is greater by a factor of:-
The height at which the weight of a body becomes th its weight on the surface of the earth (radius ), is
When you go from equator to the poles, the value of acceleration due to gravity
Assertion : A body kept inside a spherical shell does not experience any gravitational force.
Reason : The body inside a spherical shell is protected from the gravitational attraction of bodies outside the shell.
Assertion : A body falling freely under the force of gravity has constant acceleration (9.81 m/sec2).
Reason : Earth attracts every body towards its centre by the same force.
Assertion : The gravitational field of moon is much less than that of earth.
Reason : Gravitational field of a given mass () depends upon , which is smaller for moon.
Assertion : A person feels weightlessness in an artificial satellite of the earth. However a person on the moon (natural satellite) feels his weight.
Reason : Artificial satellite is a freely falling body and on the moon surface, the weight is mainly due to moon’s gravitational attraction.
Assertion :If the earth stops rotating about its axis, the value of the weight of the body at equator will decrease.
Reason : The centripetal force does not act on the body at the equator.
Assertion: If rotation of earth about its own axis suddenly stops, then acceleration due to gravity will increase at all places on the earth.
Reason: At height from the surface of earth, acceleration due to gravity is, .
Assertion: The acceleration of a particle near the earth's surface differs slightly from the gravitational acceleration, .
Reason: The earth is not a uniform sphere and because it rotates.
Assertion: The difference in the value of acceleration due to gravity at pole and equator is proportional to the square of the angular velocity of the earth.
Reason: The value of acceleration due to gravity is minimum at the equator and maximum at the pole.
Read the following statements :
: An object shall weigh more at the pole than at the equator when weighed by using a physical balance.
: It shall weigh the same at pole and equator when weighed by using a physical balance.
: It shall weigh the same at pole and equator when weighed by using a spring balance.
: It shall weigh more at the pole than at the equator when weighed using a spring balance.
Which of the above options is correct?
If the mass of the sun was ten times smaller and the universal gravitational constant were ten time larger in magnitude, which of the following is not correct?
The dependence of acceleration due to gravity at a distance from the centre of the earth, assumed to be a sphere of radius of uniform density, is as shown in figure below,
(a) 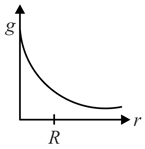 (b)
(b) 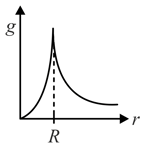
(c) 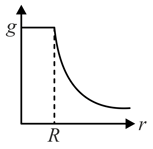 (d)
(d) 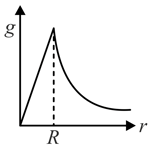
The correct figure is,
Two different masses are dropped from the same heights. When these just strikes the ground, the following is the same:
If the rotational speed of the earth is increased then the weight of a body at the equator:
More amount of sugar is obtained in weight:
The value of ’g’ reduces to half of its value at surface of earth at a height ’h’, then :-

