Reflection of Light by Mirrors
Reflection of Light by Mirrors: Overview
This topic describes the reflection of light by a plane and a spherical surface. It explains the concave and convex mirrors and terms related to the spherical mirror. It also explains the formation of images by various mirrors and their uses.
Important Questions on Reflection of Light by Mirrors
A parallel beam of light, after reflection from a mirror converges to a point. The mirror is:
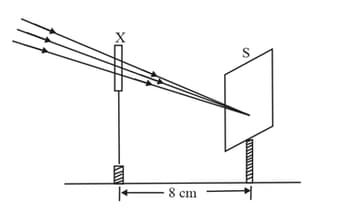
A student used his device (X) to obtain/focus the image of a well illuminated distant building on a screen (S) as shown below in the diagram. Select the correct statement about the device (X).
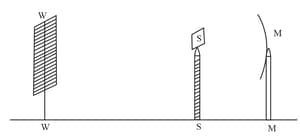
A student obtains a sharp image of the distant window (W) of the school laboratory on the screen (S) using the given concave mirror (M) to determine its focal length. Which of the following distances should be measured to get the focal length of mirror?
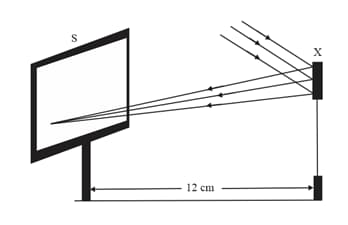
Study the following diagram and select the correct statement about the device 'X':
Parallel rays, from the top of a distant tree, incident on a concave mirror, form an image on the screen.
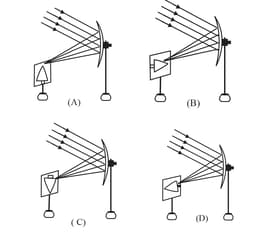
The diagram correctly showing the image of the tree on the screen is:
In the adjoining figure, 'S' is the position of the screen on which a sharp image of a distant object (nearly away from the concave mirror of focal length ) is formed by the mirror 'M'. If the object moves towards the mirror by some distance, say , then to obtain the sharp image of the object on the same screen again the
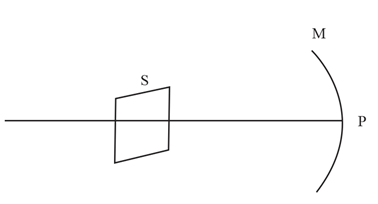
Four students measured focal length of a concave mirror while performing an experiment as shown.
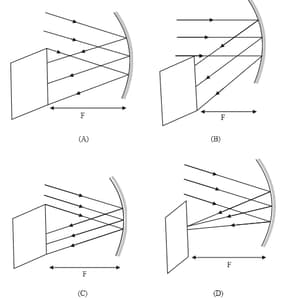
The picture which depicts the correct image formation is:
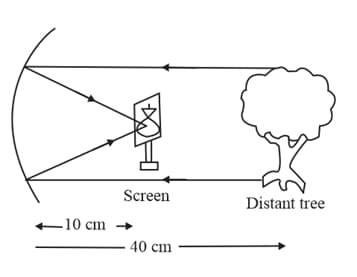
The focal length of the concave mirror in the experimental set up shown below is:
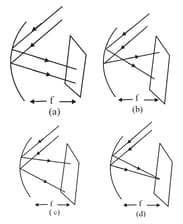
The correct ray diagram is
Which of the following ray diagrams is correct for the ray of light incident on a concave mirror as shown in the figure?
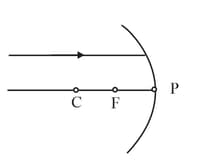
If a laser beam is allowed to fall along the principal axis of a concave mirror, the ray will:
In torches, search lights and headlights of vehicles the bulb is placed
A full length image of a distant tall building can definitely be seen by using
Rays from Sun converge at a point in front of a concave mirror. Where should an object be placed so that size of its image is equal to the size of the object?
Magnification produced by a rear-view mirror fitted in vehicles :
Under which of the following conditions a concave mirror can form a real image larger than the actual object?
A student obtained a sharp image of a candle flame placed at the distant end of the laboratory table on a screen using a concave mirror to determine its focal length. The teacher suggested him to focus a distant building, about away from the laboratory, for getting more correct value of the focal length. In order to focus the distant building on the same screen, the student should slightly move the
A ray of light falls on a plane mirror at an angle . After reflection, the angle of deviation is
To find the focal length of a concave mirror, the four students, Ram, Shamim, Kamla and Ruksana obtained the image of the window grill on a wall. They measured the distances as given below between:
Ram - Window grill and the wall only
Shamim - Window grill and the mirror only
Kamla - Mirror and wall only
Ruksana - Window grill and the wall and also between the mirror and the wall
Correct focal length will be obtained by the student.
What is the focal plane of a concave mirror?
