Lorentz Force
Important Questions on Lorentz Force
A particle of charge moves with a velocity at an angle to a magnetic field . What is the force experienced by the particle?
Write the expression, in a vector form, for the Lorentz magnetic force due to a charge moving with velocity in a magnetic field . What is the direction of the magnetic force?
What is magnetic Lorentz force?
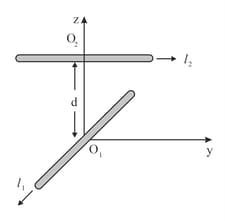
Two longitudinal wires carrying currents and are arranged as shown in figure. The one carrying current is along the -axis. The other carrying current is along a line parallel to the -axis given by and . Find the force exerted at because of the wire along the -axis.
A fine pencil of -particles, moving with a speed , enters a region (region ), where a uniform electric and a uniform magnetic field are both present. These -particles then move into region where only the magnetic field (out of the two fields present in region ), exists. The path of the -particles, in the two regions, is as shown in Figure.
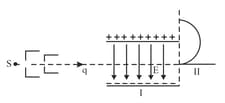
(iii) Drive the expression for the radius of the circular path of the -particle in region .
If the magnitude of magnetic field, in region , is changed to times its earlier value, (without changing the magnetic field in region ) find the factor by which the radius of this circular path would change.
A fine pencil of -particles, moving with a speed , enters a region (region ), where a uniform electric and a uniform magnetic field are both present. These -particles then move into region where only the magnetic field (out of the two fields present in region ), exists. The path of the -particles, in the two regions, is as shown in Figure.
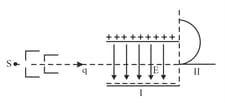
(ii) State the relation between and in region I.
If the magnitude of magnetic field, in region , is changed to times its earlier value, (without changing the magnetic field in region ) find the factor by which the radius of this circular path would change.
A fine pencil of -particles, moving with a speed , enters a region (region ), where a uniform electric and a uniform magnetic field are both present. These -particles then move into region where only the magnetic field (out of the two fields present in region ), exists. The path of the -particles, in the two regions, is as shown in Figure.
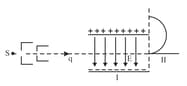
(i) State the direction of the magnetic field.
If the magnitude of magnetic field, in region , is changed to times its earlier value, (without changing the magnetic field in region ) find the factor by which the radius of this circular path would change.
A neutron, a proton, an electron and an a-particle enter a region of constant magnetic field with equal velocities. The magnetic field is along the inward normal to the plane of the paper. The tracks of the particles are labelled in Figure. Relate the tracks to the four particles.
In Figure, the straight wire is fixed while the loop is free to move under the influence of the electric currents flowing in them. In which direction does the loop begin to move ? Give reason for your answer.
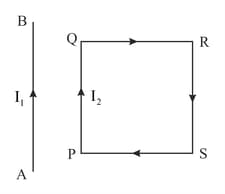
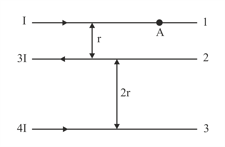
Figure shows three infinitely long straight parallel current carrying conductors. Find the (ii) magnetic force on conductor .
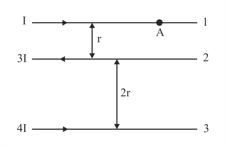
Figure shows three infinitely long straight parallel current carrying conductors. Find the
(i) magnitude and direction of the net magnetic field at point lying on conductor .
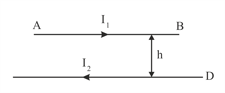
A horizontal wire of length and mass carries a steady current , free to move in vertical plane is in equilibrium at a height of over another parallel long wire carrying a steady current , which is fixed in a horizontal plane as shown. Derive the expression for the force acting per unit length on the wire and write the condition for which wire is in equilibrium.
A proton and an alpha particle of the same velocity enter in tum a region of uniform magnetic field, acting perpendicular to their direction of motion. Deduce the ratio of the radii of the circular paths described by the particles.
Two protons and moving with the same speed enter magnetic fields and respectively at right angles to the field directions. If is greater than , for which of the protons and , the circular path in the magnetic field will have a smaller radius ?
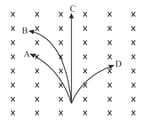
As shown in Figure, a charged particle enters a uniform magnetic field and experiences an upward force as indicated. What is the charge sign on the particle?
A beam of protons on passing through a region in space is deflected sidewise. How would you be able to tell which of the two fields (electric or magnetic) has caused the deflection ?
An electron does not suffer any deflection while passing through a region. Are you definite there is no magnetic field in that region ?
Under what condition is the force acting on a charge moving through a uniform magnetic field maximum ?
In a certain arrangement, a proton (or an electron) does not get deflected while moving through a magnetic field region. Under what condition is it possible ?
An electron moving with a velocity of enters a uniform magnetic field of , along a direction parallel to the field. What would be its trajectory in this field?

