Formation of Image by a Convex Mirror
Formation of Image by a Convex Mirror: Overview
The topic explains the formation of image by a convex mirror in detail. It lists the uses of convex mirror. It further discusses how to distinguish between a plane mirror, a concave mirror and a convex mirror without touching them.
Important Questions on Formation of Image by a Convex Mirror
A shop security mirror from certain items displayed in the shop produces one-tenth magnification.
What is the type of mirror?a
Draw a diagram to represent a convex mirror. On this diagram mark principal axis, principal focus and the centre of curvature if the focal length of convex mirror is .
A man standing in front of a special mirror finds his image having a very small head, a fat body and legs of normal size. What is the shape of top part of the mirror?
The diagrams show the appearance of a fork when placed in front of and close to two mirrors A and B turn by turn.
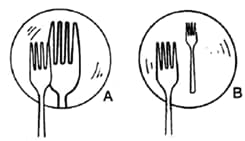
Which mirror is convex?
A boy is standing in front of and close to a special mirror. He finds the image of his head bigger than normal, the middle part of his body of the same size, and his legs smaller than normal. The special mirror is made up of three types of mirrors in the following order from top downwards:
A concave mirror cannot be used as:
If the image formed is always virtual, the mirror can be:
Whatever be the position of the object, the image formed by a mirror is virtual, erect and smaller than the object. The mirror then must be:
Draw diagram to show how a convex mirror be used to give a large field of view.
State three characteristics of the image formed when an object is placed at infinity of a convex mirror.
Draw a labelled ray diagram to show the formation of image in a convex mirror when the object is at infinity. Mark clearly the pole and focus of the mirror in the diagram.
State three characteristics of the image formed by a convex mirror.
What happens to the image when the object is moved away from the convex mirror gradually?
Draw a labelled ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object by a convex mirror. Mark clearly the pole, focus and centre of curvature on the diagram.
If a driver has one convex and one plane rear-view mirror, how would the images in each mirror appear different?
What would your image look like if you stood close to a large convex mirror?
Give two uses of a convex mirror. Explain why you would choose convex mirror for these uses.
What is the advantage of using a convex mirror as a rear-view mirror in vehicles as compared to a plane mirror? Illustrate your answer with the help of labelled diagrams.
The shiny outer surface of a hollow sphere of aluminium of radius is to be used as a mirror. State whether this spherical mirror will diverge or converge light rays.
The shiny outer surface of a hollow sphere of aluminium of radius is to be used as a mirror. Which type of spherical mirror will it provide?
