Conservative and Dissipative Forces
Important Questions on Conservative and Dissipative Forces
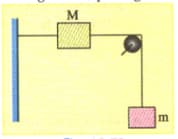
A string, with one end fixed on a rigid wall, passing over a fixed frictionless pulley at a distance of from the wall, figure below, has a point mass attached to it at a distance of from the wall. A mass attached at the free end is held at rest so that the string is horizontal between the wall and the pulley and vertical beyond the pulley. What will be the speed with which the mass will hit the wall when the mass is released? (Take ).
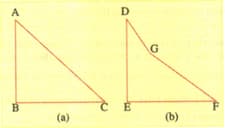
In the below figure (a) and (b) and are fixed inclined planes, and . A small block of mass is released from the point . It slides down and reaches with a speed . The same block is released from rest from the point . It slides down and reaches the point with speed . The coefficient of friction between the block and both surfaces and are . Calculate and .
A bullet pierces through a plate of mass and then come to rest inside a second plate of mass as shown in figure below. It is found that two plates initially at rest, now move with equal velocities. Find the percentage loss in initial velocity of the bullet when it is between and . Neglect any loss of material of the plates due to action of the bullet.
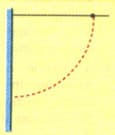
A simple pendulum is suspended from a peg on a vertical wall. The pendulum is pulled away from the wall to a horizontal position, see figure below and released. The ball hits the wall, the coefficient of restitution being . What is the minimum number of collisions after which the amplitude of oscillations becomes less than ?
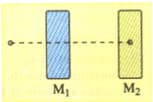
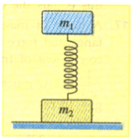
Two plates of masses and are connected by a spring of force constant , figure below. What force should be applied to the upper plate for it to raise the lower one after the force is removed? Disregard the mass of the spring.
A ball with a speed of strikes another identical ball such that after collision the direction of each ball makes an angle with the original line of motion. Find the speeds of the two balls after the collision. Is the kinetic energy conserved in this collision process?
A body slides from the point , figure along a horizontal track with an initial speed of towards a weightless horizontal spring of length and force constant . The part of the track is frictionless and the part has the coefficient of static and dynamic friction and respectively. Find the total distance through which the block moves before it comes to rest completely , if and .
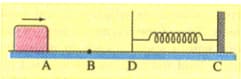
A body of mass is being dragged with a uniform velocity of on a rough horizontal plane. The coefficient of friction between the body and the surface is . Calculate the amount of work done in .( )
The potential energy of a mass free to move along the -axis is given by . The total mechanical energy of the mass is . Find the maximum speed of the mass.
An upward force newton is applied upon a body of mass till it is raised vertically upward by a distance against gravity. Here the work done by is much greater than the gain in gravitational P.E. Show using clear calculations that the law of conservation of energy is quantitatively satisfied here.
A bullet of mass travelling horizontally at embeds itself in the centre of a block of wood of mass which is suspended by a light vertical string in length. Calculate the maximum inclination of the string to the vertical. .
A bullet of mass moving at a speed of is stopped inside a wooden block of mass initially at rest on a smooth horizontal table. Find the final velocity of the block. What are the initial and final energies of the system (block+bullet)?
A body of mass fell from a height of on to a peg. If the peg penetrates into the ground, calculate the resistive force of the ground in newtons.
A boy pulls a block along a horizontal surface at a constant speed through a distance of . What work does he do on block if the co- of kinetic friction between the block and the surface is and his pull makes an angle of with the horizontal?
Differentiate between gravitational potential energy and elastic potential energy. Obtain an expression for the strain energy of a stretched spring of unstretched length .
What are conservative and non-conservative forces? Give reasons why the force of gravity is a conservative force but frictional force is a non-conservative force.
Work done in the motion of a body over a closed loop is zero for every force in nature.
Give two examples of conservative forces.
Give two examples of non-conservative forces.
Give two examples of conservative forces.

