Angular Dispersion and Dispersive Power
Angular Dispersion and Dispersive Power: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Dispersive Power, Dispersion without Deviation in Prism, Deviation without Dispersion in Prism, and Angular Dispersion.
Important Questions on Angular Dispersion and Dispersive Power
It is desired to make an achromatic combination of two lenses and . If the combination of lenses is converging then
The refractive indices of flint glass prism for violet, yellow and Red colours are , and respectively, find dispersive power of the flint glass. (upto five decimal places)
A thin prism P1 with angle and made from glass of refractive index is combined with another thin prism P2 made from glass of refractive index to produce dispersion without deviation. What is the angle of prism in degree ?
Define deviation without dispersion.
Two thin prisms are combined of refractive indexes . The combination of the prisms produces dispersion without deviation. The angle of the first prism is . Find the angle for second prism.
A thin prism P1 with angle and made from glass of refractive index is combined with another thin prism P2 made from glass of refractive index to produce dispersion without deviation. What is the angle of prism in degree ?
Calculate the dispersive power for crown glass from the given data
and
The respective angles of the flint and crown glass prisms are and . They are to be used for dispersion without deviation, then the ratio of their angles will be
The following data are given for a crown glass prism, refractive index for violet light nv = 1.521, refractive index for red light nr = 1.510 and refractive index for yellow light ny = 1.550. Dispersive power of a prism is
The following data are given for a crown glass prism, refractive index for violet light , refractive index for red light and refractive index for yellow light . Dispersive power of a prism is
A prism of certain angles deviates the red and violet rays by and respectively. Another prism of the same angle deviates the red and violet rays by and respectively. The prisms are small angled and made of different materials. The dispersive powers of the materials of the prism are in the ratio
An achromatic lens is made using a convex and a concave lens. The power of the achromatic convergent lens of two lenses is . The power of convex lens is . The ratio of dispersive power of convex and concave lenses will be
Three thin prisms are combined as shown in diagram. The refractive indices of the crown glass for red and violet rays are and respectively and those for the flint glass are and respectively. The ratio for which there is no net angular dispersion
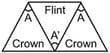
Three thin prisms are combined as shown in diagram. The refractive indices of the crown glass for red and violet rays are and respectively and those for the flint glass are and respectively. The ratio for which there is no net angular dispersion
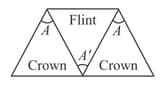
Dispersive powers of materials used in lenses of an achromatic doublet are in the ratio 5:3. If the focal length of concave lens is 15 cm, then the focal length of the other lens will be
The two lenses of an achromatic doublet should have
The refractive indices of the crown glass for blue and red light are 1.51 and 1.49 respectively and those of the flint glass are 1.77 and 1.73 respectively. An isosceles prism of angle 60 is made of crown glass. A beam of white light is incident at a small angle on this prism. The other flint glass isosceles prism is combined with the crown glass prism such that there is no deviation of the incident light.
Calculate the net dispersion of the combined system.
