Reflection by Spherical Mirrors
Reflection by Spherical Mirrors: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Image Formation by a Spherical Mirror, Curved Mirrors, Spherical Mirrors, Mirror Formula & Magnification in Spherical Mirror etc.
Important Questions on Reflection by Spherical Mirrors
For magnification in spherical mirrors, the object height is taken:
An object of height is placed in front of a concave mirror and virtual image of height is obtained. If the object is placed at from the concave mirror, the focal length of mirror is
Correct relation between radius of curvature() and Focal length () of a spherical mirror is:
An object is placed at a distance of . From a convex mirror of focal length . The position and nature of the image are :
_____ is located behind a convex mirror :
In the following diagram ‘’ is a mirror and ‘’ is an object and ‘’ is the magnified image of ‘’ formed by the mirror. The mirror ‘’ is a:
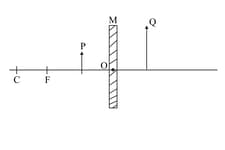
A spherical mirror and a thin spherical lens each of focal length are given. The mirror and lens are likely to be:
Which of the following mirror is used by a dentist to examine the patient tooth?
A concave mirror of focal length 15cm forms an image. The position of the object when the image is virtual and linear magnification is 2 is.
The image formed by a concave mirror is observed to be virtual, erect and larger than the object. Where should be the position of the object?
The ratio of the focal length of spherical mirror to its radius of curvature is
An object placed at the centre of curvature of concave mirror. Its image is formed at :
At focus and between and , a concave mirror always forms a
Among the following an example for extended source of light is
Following are the examples for point sources of light.
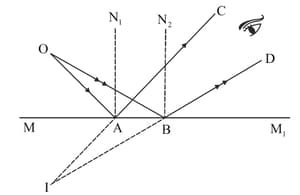
In the diagram given below, the image formed is
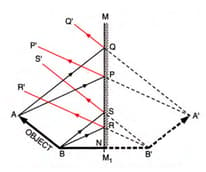
The image formed in the diagram given below is
An object is placed in front of convex mirror at a distance of 50 cm. A plane mirror is introduced covering the lower half of the convex mirror. If the distance between the object and plane mirror is 30 cm. It is found that there is no parallax between the images formed by two mirrors. Radius of curvature will be
A candle flame 3 cm is placed at a distance of 3 m from a wall. How far from wall must a concave mirror be placed in order that it may form an image of flame 9 cm high on the wall
