Refraction at Plane Surfaces
Refraction at Plane Surfaces: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Refraction of Light, Absolute Refractive Index, Refracted Ray, Snell's Law, Relative Refractive Index, Refraction from Plane Surface, Refraction from Single Slab, Apparent Depth for One Liquid, etc.
Important Questions on Refraction at Plane Surfaces
A ray of light moving along the unit vector undergoes refraction at an interface of two media, which is the plane. The refractive index for is while for , it is . The unit vector along which the refracted ray moves is
A parallel sided block of glass of refractive index which is thick rests on the floor of a tank which is filled with water (refractive index). The difference between the apparent depth of floor at and when seen from vertically above is equal to
A ray of sunlight enters a spherical water droplet () at an angle of incidence measured with respect to the normal to the surface. It is reflected from the back surface of the droplet and re-enters into the air. The angle between the incoming and outgoing ray is [Take ]
A surveyor on one bank of canal observed the image of the 4 inch and 17 ft marks on a vertical staff, which is partially immersed in the water and held against the bank directly opposite to him, coincides. If the 17 ft mark and the surveyor's eye are both 6 ft above the water level, If the width of the canal is 10 + x, assuming that the refractive index of the water is 4/3, then find the value of x. Zero mark is at the bottom of the canal.
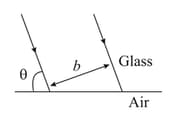
A beam of parallel rays of width b propagates in glass at over to air this face is _________ if the refractive index of glass is μ.v
When light travels from a rarer to a denser medium, which of the following parameter of light decreases:
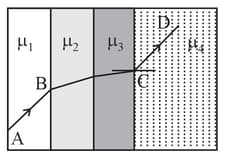
A ray of light passes through four transparent media with refractive indices and as shown in the figure. The surfaces of all media are parallel. If the emergent ray is parallel to the incident ray , we must have
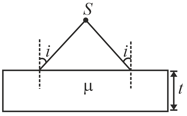
A diverging beam of light from a point source S having divergence angle , falls symmetrically on a glass slab as shown. The angles of incidence of the two extreme rays are equal. If the thickness of the glass slab is t and the refractive index n, then the divergence angle of the emergent beam is
A monochromatic beam of light of wavelength in vacuum enters a medium of refractive index . In the medium its wavelength is __________, its frequency is ____________
When a ray of light enters a glass slab from air
A light of wavelength in air, enters a medium with refractive index . Inside the medium its frequency is and its wavelength is_______ .
If and are, respectively, the electric permittivity and magnetic permeability of free space, and the corresponding quantities in a medium, the index of refraction of the medium in terms of the above parameters is
A light wave of frequency enters a medium of refractive index . In the medium the velocity of the light wave is ________________ and its wavelength is ______________
A metal coin is at the bottom of a beaker filled with a liquid of refractive index to height of . To an observer looking from above the surface of the liquid, coin will appear at a depth of
A plane glass is placed over various coloured letters (violet, green, yellow, red). The letter which appears to be raised more is:
If the difference in the velocities of light in glass and water is , velocity of light in air is
(Given that refractive index of glass and water with respect to air are and respectively.)
A ray of light is incident at an angle on a glass slab. If the angle of refraction is . Find the refractive index of glass.
Why sun appears reddish at sunrise and sunset?
For equal angle of incidence, refraction angle for these media and are , and respective. In which medium speed of light is minimum?
What is cause of refraction ?
