Combinations of Mirrors and Thin Lenses
Combinations of Mirrors and Thin Lenses: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Thin Lenses in Contact, Silvered Lens & Cutting of Lens etc.
Important Questions on Combinations of Mirrors and Thin Lenses
Which of the following can form diminished, virtual and erect image of your face
A flat mirror is arranged parallel to the wall at a distance from it. The light produced by a point source kept on the wall is reflected by the mirror and produces a light spot on the wall. The mirror moves with velocity towards the wall.
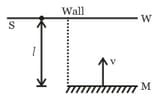
It is desired to make an achromatic combination of two lenses and . If the combination of lenses is converging then
A planoconvex lens, when silvered at its plane surface is equivalent to a concave mirror of focal length . When its curved surface is silvered and the plane surface not silvered, it is equivalent to a concave mirror of focal length , then the refractive index of the material of the lens is
An object is placed in front of a thin convex lens of focal length 30 cm and a plane mirror is placed 15 cm behind the lens. If the final image of the object coincides with the object, the distance of the object from the lens is
A object is placed at a distance of 15 cm from a convex lens of focal length 10 cm. On the other side of the lens, a convex mirror is placed at its focus such that the image by the combination coincides with the object itself. The focal length of the convex mirror is
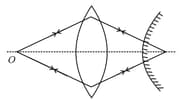
A double convex lens has focal length of in air. The radius of one of the surfaces is double of the other. Find the radii of curvature, if the refractive index of the material of the lens is .
Which of the following expression is correct for :
Taking the rays as incident from a medium of refractive index to another of refractive index
An illuminated object and a screen are placed apart. The focal length and nature of the lens required to produce a clear image on the screen, twice the size of the object would be:
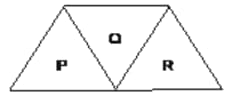
A given ray of light suffers minimum deviation in an equilateral prism . Additional prism and of identical shape and of the same material as are now added as shown in the figure. The ray will now suffer
An eye specialist prescribes spectacles having a combination of convex lens of focal length 40 cm in contact with a concave lens of focal length 25 cm. The power of this lens combination in diopters is
Spherical aberration in a thin lens can be reduced by
A thin plane convex glass lens has its plane surface silvered and is the radius of curvature of the curved part. Then which of the following ray diagram is the correct representation for an object placed at .
A biconvex lens of radius of curvature is made up of a variable refractive index . Assume . A point object is placed at on the principal axis as shown in figure. If the spread of image lies over a span of meter along the axis, then find the value of .
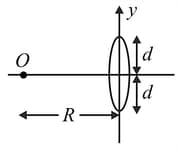
The radius of curvature of convex surface of a Plano-convex lens is . The of material of lens is . When kept in air has focal length . If plane surface is silvered and lens is kept in a large medium of , it behave as a mirror of power
A tube of length has its inner lateral surface blackened. Two lenses of focal lengths and are fixed at the ends of the tube. For same beam, intensities of spots on screen are and for arrangement and arrangement . If the ratio of is of the form find .
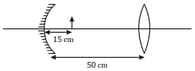
A real image of an object is formed at a distance of from a lens. On putting another lens in contact with it, image is shifted towards the combination. The power of the lens is _____ .
Consider a concave mirror and a convex lens (refractive index = ) of focal length each, separated by a distance of in air (refractive index = ), as shown in the figure. An object is placed at a distance of from the mirror. Its erect image, formed by this combination, has magnification . When the set-up is kept in a medium of refractive index , the magnification becomes . The magnitude is
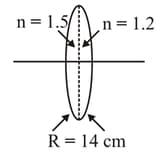
A bi-convex lens is formed with two thin plano-convex lenses as shown in the figure. The refractive index of the first lens is and that of the second lens is . Both the curved surfaces are of the same radius of curvature, . For this bi-convex lens, for an object distance of , the image distance will be,
A combination of two thin convex lenses of focal length and will have minimum spherical and chromatic aberrations if
the distance between them is
