Reflection of Light at Spherical Mirrors
Reflection of Light at Spherical Mirrors: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Spherical Mirror, Pole of Spherical Mirror, Image Formation in Combination of Plane and Spherical Mirrors & Image in Two Spherical Mirrors etc.
Important Questions on Reflection of Light at Spherical Mirrors
A luminous point object is placed at , whose images is formed at as shown in the figure. is the optical axis. Which of the following statements are correct?
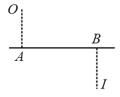
The circular boundary of the concave mirror subtends a cone of half angle at its centre of curvature. The minimum value of for which ray incident on this mirror parallel to the principle axis suffers reflection more than one is
A point source of light is 60 cm from a screen and is kept at the focus of a concave mirror which reflects light on the screen. The focal length of the mirror is 20 cm. The ratio of average intensities of the illumination on the screen when the mirror is present and when the mirror is removed is:
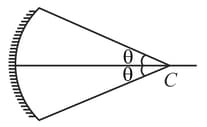
In the figure shown if the object 'O' moves towards the plane mirror, then the image I (which is formed after successive reflections from M1 & M2 respectively) will move:
A luminous point object is moving along the principal axis of a concave mirror of focal length 12 cm towards it. When its distance from mirror is 20 cm its velocity is 4 cm/s. The velocity of the image in cm/s at that instant is:
An infinitely long rod lies along the axis of a concave mirror of focal length . The near end of the rod is at a distance from the mirror. Its image will have a length
In the figure shown, the image of a real object is formed at point I. AB is the principal axis of the mirror. The mirror must be:

A thin road of length d/3 is placed along the principal axis of a concave mirror of focal length = d such that its image, which is real and elongated, just touches the rod. Find the length of the image?
If object is at distance from silvered plano convex lens whose refractive index is . Image is also formed at a distance of. What is radius of curvature: (Consider it is a thin lens)
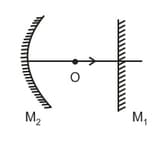
An object is moving with in front of a convex mirror () as shown in figure. Find speed of image if the mirror is stationary
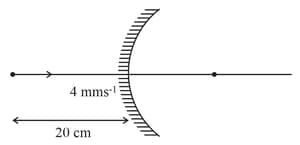
An object and a concave mirror of focal length both move along the principal axis of the mirror with constant speeds. The object moves with speed towards the mirror with respect to a laboratory frame. The distance between the object and the mirror at a given moment is denoted by . When , the speed of the mirror is such that the image is instantaneously at rest with respect to the laboratory frame, and the object forms a real image. The magnitude of is____
In the figure shown, the speed in of image with respect to mirror is:
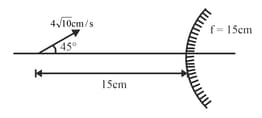
Two concave mirrors are placed apart and facing each other. A point object lies between them at a distance of from the mirror of focal length . The other mirror has a focal length of . Find the location of final image formed after two reflections- first at the mirror nearer to the object and second at the other mirror.
Find the distance between mirrors for which image and object are produced at same position after two reflections.
An object approaches a convex mirror of focal length with speed what will be velocity of image when object is from the mirror:-
Incident parallel rays make an angle of with the axis of a concave mirror of focal length at pole of the mirror. The perpendicular distance of image from the axis is nearly.
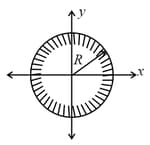
The cross-section of a reflecting surface is represented by the equation as shown in the figure. A ray travelling in the positive direction is directed towards positive direction after reflection from the surface at point . The coordinate of the point on the reflecting surface is
A source kept at focus of a parabolic mirror as shown emits rays out of which two are shown striking the parabola at and . Find the length of extra path travelled by the ray striking at than that at before striking at the mirror . ( and and options in SI units)
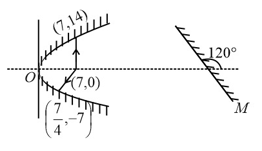
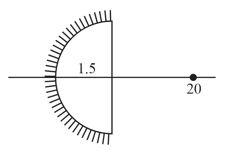
If image of '' is formed at '' itself find values of ''.
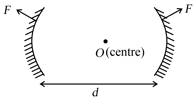
Which of the following statement is correct while using the mirror equation , when the object is kept on the left side of the mirror on the principal axis?(use real positive sign convention)

