Refraction and Dispersion of Light through Prism
Refraction and Dispersion of Light through Prism: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Angle of Prism, Deviation from Small Angle Prism, Condition of No Emergence in Prism & Chromatic Aberration etc.
Important Questions on Refraction and Dispersion of Light through Prism
It is desired to make an achromatic combination of two lenses and . If the combination of lenses is converging then
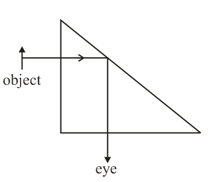
A thin prism of angle is placed at a distance of from the object. The distance of the image from the object is (given of prism)
A prism has a refractive index and refracting angle . Find the minimum deviation produced by prism
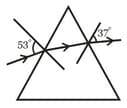
A ray incident at angle 53o on a prism emerges at an angle at 37o as shown. If the angle of incidence is made 50o, which of the following is a possible value of the angle of emergence.
A parallel beam of light falls normaly on the first face of a prism of small angle. At the second face it is partly transmitted and partly reflected, the reflected beam striking at the first face again, and emerging from it in a direction making an angle 6o 30' with the reversed direction of the incident beam. The refracted beam is found to have undergone a deviation of 1o 15' from the original direction. Find the refractive index of the glass and the angle of the prism.
The refractive indices of the crown glass for violet and red lights are and respectively and those of the flint glass are and respectively. A prism of angle is made of crown glass. A beam of white light is incident at a small angle on this prism. The other thin flint glass prism is combined with the crown glass prism such that net mean deviation is anticlockwise.
A screen is placed normal to the emerging beam at a distance of from the prism combination. Find the distance between red and violet spot on the screen. Which is the topmost colour on screen.
How does the angle of minimum deviation of a glass prism vary, if the incident violet light is replaced with red light?
A ray of light undergoes deviation of when incident on an equilateral prism of refractive index What is the angle subtended by the ray inside the prism with the base of the prism is ?
Which one of the following spherical lenses does not exhibit dispersion? The radii of curvature of the surfaces of the lenses are as given in the diagrams.
Which one of the following spherical lenses does not exhibit dispersion? The radii of curvature of the surfaces of the lenses are as given in the diagrams.
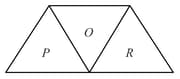
A given ray of light suffers minimum deviation in an equilateral prism . Additional prism and of identical shape and of the same material as are now added as shown in the figure. The ray will now suffer
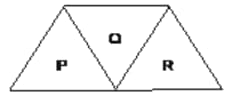
A given ray of light suffers minimum deviation in an equilateral prism . Additional prism and of identical shape and of the same material as are now added as shown in the figure. The ray will now suffer
Spherical aberration in a thin lens can be reduced by
A ray of light is incident normally on one of the faces of a prism of apex angle and refractive index . The angle of deviation of the ray is
The refractive index of a transparent liquid filled in an equilateral hollow prism is . The angle of minimum deviation for the liquid will be _______.
The refractive index of equilateral prism is , then find its minimum angle of deviation (in degree).
At what maximum angle should a ray of light be incident on the face of a prism of refracting angle so that it just suffers total internal reflection at the other face? The refractive index of the material of the prism is .
A ray coming from an object is reflected totally at the slant surface of the prism. The possible orientation of the image is
I) The speed of light does not depend upon the nature of medium through which it passes.
II) The beam of light is deviated or refrected from its original path as it passes from one medium to another.
III) When a ray of light is passed through a prism, the wave with shorter wavelength bends more than one with longer wavelength.
Which of the following statements is true?
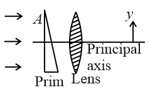
A parallel beam is incident on to a lens of focal length (positive), parallel to its principal axis. A thin prism of vertex angle and refractive index is inserted in the path of the parallel beam before it falls on the lens. The focal point of the image