Refraction of Light at Plane Surface
Refraction of Light at Plane Surface: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Refraction from Plane Surface, Refraction from Single Slab, Refraction from Multiple Glass Slab, Deviation in Refraction, Apparent Depth for One Liquid, etc.
Important Questions on Refraction of Light at Plane Surface
A parallel sided block of glass of refractive index which is thick rests on the floor of a tank which is filled with water (refractive index). The difference between the apparent depth of floor at and when seen from vertically above is equal to
A bird is flying 3 m above the surface of water. If the bird is diving vertically down with speed = 6 m/s, his apparent velocity as seen by a stationary fish underwater is:
A point object is placed at a distance of from a convex lens of focal length . If a glass slab of thickness and refractive index is inserted between the lens and object. The image is formed at infinity. Find the thickness .
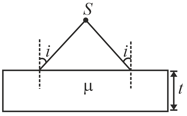
A diverging beam of light from a point source S having divergence angle , falls symmetrically on a glass slab as shown. The angles of incidence of the two extreme rays are equal. If the thickness of the glass slab is t and the refractive index n, then the divergence angle of the emergent beam is
Consider a ray of light passing through a rectangular slab of refractive index and thickness as shown below.
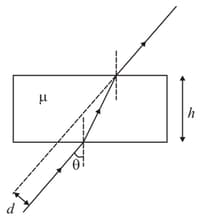
This leads to a parallel shift in the path of the ray, which varies between to as varies. How does change with
The angle of deviation produced by the glass slab is
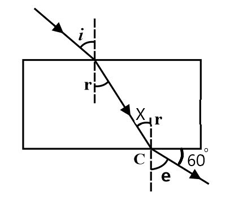
For a certain parallel-sided glass block, the value of is . A ray of light passes through the block and emerges at an angle of to the surface of the block. What is the value of the angle marked X?
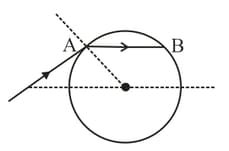
What should be the angle of incidence at A of the spherical glass placed in air so that so that grazing emergence of light ray takes place at
Consider the situation shown in figure. Water is filled in a beaker upto a height of . A plane mirror is fixed at a height of from the surface of water. Distance of image from the mirror after reflection from it of an object at the bottom of the beaker is :-
In the figure shown the angle made by the light ray with the normal in the medium of refractive index is :-
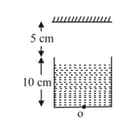
A tank is filled with water to a height of The apparent depth of a coin placed at the bottom is measured by a microscope to be What is the refractive index of water? If water is replaced by a liquid of refractive index up to the same height, then by what distance would the focus of microscope has to be shifted to see the coin again?
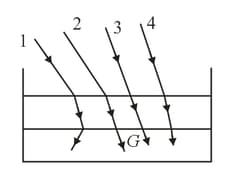
The optical density of turpentine is higher than that of water while its mass density is lower. Figure shows a laycr of turpcntine floating over water in a container. For which one of the four rays incident on turpentine in figure, the path. shown is correct
A glass beaker is filled with water up to It is kept on top of a thick glass slab. When a coin at the bottom of the glass slab is viewed at the normal incidence from above the beaker, its apparent depth from the water surface is . Value of is close to (the refractive indices of water and glass are and , respectively)
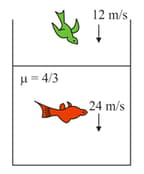
A fish and a bird are moving as shown in figure. Find the velocity of bird as observed by fish.
The apparent depth of needle lying at the bottom of the tank which is filled with water to a height of is measured by a microscope to be . If water is replaced by a liquid of refractive index to the same height as earlier, compute the displacement of the microscope needed to establish focus on the needle again.
If light is refracted from a plane surface while passing from a denser medium to rarer medium, then which of the following statements is/are correct about it. [ is critical angle]
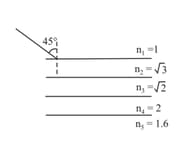
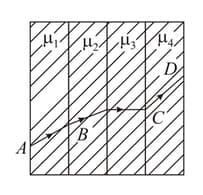
A ray of light passes through four transparent media whose surfaces are parallel to each other with refractive indices . If the emergent ray, is parallel to the incident ray , then, which of the following relations should be correct?
A ray of light is incident on a surface of glass slab at an angle The angle of refraction if the lateral shift produced per unit thickness is
Three immiscible liquids of densities and refractive indices are put in a beaker. The height of each liquid column is . A dot is made at the bottom of the beaker. For near normal vision, find the apparent depth of the dot.
A vessel of depth is half filled with oil of refractive index and the other half is filled with water of refractive index . The apparent depth of the vessel when viewed from above is
