Basic Terms in Geometrical Optics
Basic Terms in Geometrical Optics: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Optics, Geometrical Optics, Ray of Light, Beam of Light, Wave Theory of Light, Fermat's Principle, and Principle of Reversibility.
Important Questions on Basic Terms in Geometrical Optics
A man of height is walking away from a street lamp with a constant speed . The height of the street lamp is . The rate at which of the length of the man's shadow is increasing when he is at a distance from the base of the street lamp is:
Is light a ray or a wave?
What is difference between ray of light and beam of light?
What do we call a single ray of light?
Who produced Ray of Light by Madonna?
A beam of light is generated by a laser is called-
The ray from the sun is an example of a parallel beam of light.
When a light ray after suffering any number of reflections and refractions, its final path has reversed, it travels back along its entire initial path.
Refractive index of a medium depend upon the temperature of the medium.
Write the Huygen's principle of wave theory of light?
Which of the following phenomenon can not be explained using wave theory of light?
Which of the following phenomenon is studied under ray optics?
Differentiate between ray optics and wave optics.
What do you understand by the term "optics"?
The following graph depicts the inverse of magnification versus the distance between the object and lens data for a setup. The focal length of the lens used in the setup is
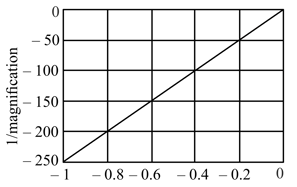
Distance between the object and the lens
Name the branch of physics which deals with the formation of images by mirrors and lenses.
A Spider and a fly are on the surface of a glass sphere. Where must the fly be for the spider to be able to see it. Assume that radius of sphere much larger than their size and RI of sphere
Newton postulated his corpuscular theory on the basis of _______.
Assertion: For a point light source, frequency of light emitted is numerically equal to number of photons emitted per second.
Reason: According to wave theory frequency of light wave is equivalent to number of cycles completed per second and wave-particle duality explains the dual nature of electromagnetic waves as a wave or as a corpuscle.
Assertion: Geometrical optics can be regarded as the limiting case of wave optics.
Reason: When the size of the obstacle or opening is very large compared to the wavelength of light then wave nature can be ignored and light can be assumed to be traveling in a straight line.
