Refraction of Light by Curved Surfaces
Refraction of Light by Curved Surfaces: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Refraction from Spherical Surface & Power of a Spherical Refracting Surface etc.
Important Questions on Refraction of Light by Curved Surfaces
A spherical thick shell made of transparent material is cut along its chord as shown. The smaller part will
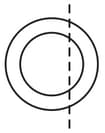
A beam of diameter 'd' is incident on a glass hemisphere as shown. If the radius of curvature of the hemisphere is very large in comparison to d, then the diameter of the beam at the base of the hemisphere will be
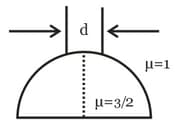
A beam of diameter is incident on a glass hemisphere as shown. If the radius of curvature of the hemisphere is very large in comparison to , then the diameter of the beam at the base of the hemisphere will be
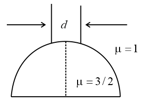
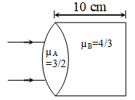
A concave spherical surface of radius of curvature 10 cm separates two medium x & y 0f refractive index 4/3 & 3/2 respectively. If the object is placed along principal axis in medium X then
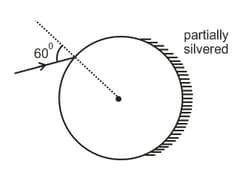
A ray is incident on a glass sphere as shown. The opposite surface of the sphere is partially silvered. If the net deviation of the ray transmitted at the partially silvered surface is 1/3rd of the net deviation suffered by the ray reflected at the partially silvered surface (after emerging out of the sphere). Find the refractive index of the sphere.
A thin lens of refractive index has a focal length of in air. When the lens is placed in a medium of refractive index its focal length will become _________ .
A small point objects is placed in air at a distance of from a convex spherical refractive surface of If radius of curvature of spherical surface is , calculate the position of the image and the power of the refracting surface.
Write the formula for the refraction of light on a spherical surface. Establish lens formula with its help. Symbols used their usual meanings.
How do you find the power of a refracting surface.
What is power of refracting surface
What is the unit of measurement of refracting power of a spherical surface.
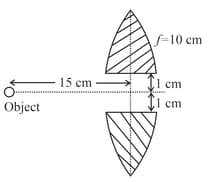
A point object is placed as shown. The two identical half pieces of the same lens of focal length are separated by as shown. Find the distance (in ) between the two images formed by the two pieces of the lens.
The radius of curvature of each surface of an equiconvex lens is Refractive index of the glass If the final image forms after four internal reflections (But not ) inside the lens (for paraxial incident beam) calculate the distance (in ) of the image from the lens.
In the given figure, a plano-concave lens is placed on a paper on which a flower is drawn. The distance above its actual position at which the flower appear to be is
Let the focal length of a lens of refractive index be in air. What will be the focal length of that lens in a medium of refractive index ?
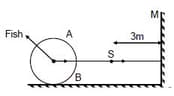
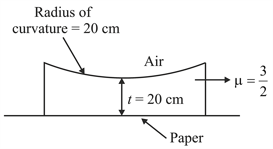
A thin walled sphere made up of glass is fixed on a horizontal surface. The radius on the sphere is and it is filled with a transparent liquid of refractive index is the luminous source moving directly towards a plane vertical mirror . A fish in the liquid is moving towards . The eye of the fish and are collinear and perpendicular to mirror . At the moment is $3 \mathrm{m}$ away from the centre of the sphere, the fish observes that image of due to reflection is moving with a speed of If speed of the fish relative to the sphere is and then what will be the speed of the source at that instant? (The system is placed in air)
Cotyledons are also called-
A parallel paraxial beam of light is incident on the arrangement as shown. , , the two spherical surfaces are very close and each has a radius of curvature . Find the point where the rays are focussed. (w.r.t. point of entry)
A small object of length 1 mm lies along the principal axis of a spherical glass of radius R = 10 cm and refractive index is 3/2. The object is seen from air along the principal axis from left. The distance of object from the centre is 5 cm. Find the size of the image in mm.
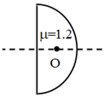
A plastic hemisphere has a radius of curvature of 8 cm and an index of refraction of 1.2. On the axis half way between the plane surface and the spherical one (4 cm from each) is a small object O. The distance between two images when viewed along the axis from the two sides of the hemisphere is approximately in cm.