Interference of Light
Interference of Light: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Properties of Light Waves, Coherence of Light Waves, Types of Coherence, Temporal Coherence, Spatial Coherence, Coherent Light Wave Production, Division of Wave Front, and Division of Amplitude.
Important Questions on Interference of Light
In Young’s double slit experiment, the two slits 0.15 mm apart are illuminated by monochromic light of wavelength 450 nm. The screen is 1.0 m away from the slits.
(a) Find the distance of the second (i) bright fringe, (ii) dark fringe from the central maximum.
Which of the following expressions is/are correct for Young’s experiment?
(i) condition for bright fringes
(ii) condition for dark fringes
ii) fringe width
A point source emits sound equally in all directions in a non-absorbing medium. Two points P and Q are at a distance of 9 metres and 25 metres respectively from the source. The ratio of amplitudes of the waves at P and Q is ___________
A thin slice is cut out of a glass cylinder along a plane parallel to its axis. The slice is placed on a flat glass plate as shown in figure. The observed interference fringes from this combination shall be
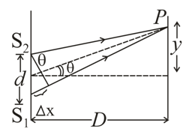
In an interference arrangement similar to Young’s double-slit experiment, slits are illuminated with coherent microwave sources each of frequency 1 MHz. The sources are synchronized to have zero phase difference. The slits are separated by distance d = 150.0 m. The intensity is measured as a function of where is defined as shown in figure. If is maximum intensity, calculate for
Two coherent monochromatic light beams of intensities and are superposed. The maximum and minimum possible intensities in the resulting beam are
Two coherent monochromatic light beams of intensities and are superposed. The maximum and minimum possible intensities in the resulting beam are
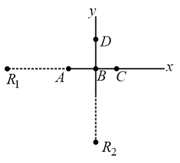
Consider four identical monochromatic wave sources (as shown in the figure) which produce plane waves of same wavelength . Sources and lie in a line, with at the origin and being from the origin. Initially the source is at a distance from the origin but later it is moved to a distance from the origin. Two receivers and are kept at equal large distance from the origin. Select the correct option(s).
White light with uniform intensity across the visible wavelength range of to is incident almost perpendicularly from above onto a horizontal liquid film of refractive index and of thickness . The medium on both sides of the film is air. The wavelength of light reflected by the film which appears brightest to an observer seeing it from the top is close to
What do you understand by spatial and temporal coherence assignment expert?
What is difference between coherent and incoherent light?
How is temporal coherence related to Monochromaticity?
What is the nature of central fringe in Lloyd's mirror experiment?
How the fringes produced by Biprism and Lloyd's mirror set up are different?
What are the important advantages of Lloyd's mirror over double slit interferometers?
Zero order fringe can be identified using _____
