Polarisation by Reflection
Polarisation by Reflection: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Polarisation by Reflection, Polarising Angle, Brewster's Law, Angle of Incidence Greater than Polarising Angle, Angle of Incidence Equal to Polarising Angle, and Angle of Incidence Less than Polarising Angle.
Important Questions on Polarisation by Reflection
A ray of light is incident at polarizing angle such that its deviation is , then angle of incidence is
Identify the correct path of light rays when angle of incidence is greater than critical angle:
The reflected light will be linearly polarised:
If a light beam is an incident at a polarizing angle on the air-glass interface, then what is the angle of refraction in the glass?
A ray of light is incident on the surface of a glass plate at an angle of incidence equal to Brewster's angle . If represents the refractive index of glass with respect to air, then the angle between reflected and refracted rays is
The angle of incidence of light at the interface of two dielectric media which results into zero reflection is called
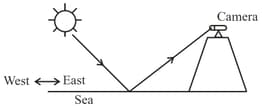
A camera filled with a polarizer is placed on a mountain, in a manner to record only the reflected image of the sun from the surface of a sea as shown in the figure. If the sun rises at and sets at during the summer, then at what time in the afternoon will the recorded image have the lowest intensity, assuming there are no clouds and intensity of the sun at the sea surface is constant throughout the day? (Refractive index of water )
A ray of light strikes a glass plate at an angle . If the reflected and refracted rays are perpendicular to each other, the refractive index of the glass is:
What is the angle of polarisation and obtain an equation for angle of polarisation
A beam of light strikes a piece of glass at an angle of incidence of and the reflected beam is completely plane polarised. The refractive index of the glass is -
Unpolarised red light is incident on the surface of a lake at incident angle . An observer seeing the light reflected from the water surface through a polariser notices that on rotating the polariser, the intensity of light drops to zero at a certain orientation. The red light is replaced by unpolarised blue light. The observer sees the same effect with reflected blue light at incident angle .
Then,
When light is incident at on a transparent sheet, the reflected light is completely polarised. Find the refractive index of the substance. Round it to one digit after the decimal point.
beam of light is incident on glass slab of refractive index in direction as shown in the figure. The reflected light is analysed by a polaroid prism. On rotating the polaroid
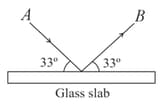
Unpolarised light of intensity is incident on surface of a block of glass at Brewster's angle. In that case, which one of the following statements is true?
Light is incident on a glass surface at polarizing angle of . Then the angle between the incident ray and the refracted ray is
The angle of incidence of light at the interface of two dielectric media which results into zero reflection is called
A ray of light is incident at an angle on surface of a glass slab of refractive index . The angle between reflected and refracted light is . Then the relationship between is
Match Column I and Column II
| Column – I | Column – II |
| (i) Interference | (P) Coherent sources |
| (ii) Brewster’s Law | (Q) |
| (iii) Malus Law | (R) |
| (iv) Total internal reflection | (S) |
At what angle of incidence, the light reflected from a glass slab will become completely polarized. The angle of refraction at that incident angle is .
