Interference of Sound Waves
Interference of Sound Waves: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Condition for Constructive Interference, Condition for Destructive Interference, Interference of Sound Waves, Equation of Resultant Sound Wave after Interference & Quincke's Tube etc.
Important Questions on Interference of Sound Waves
Select the wrong statement about the phenomenon of interference?
Find the amplitude of two sound waves of the same amplitude, each of travelling in the same direction. The phase difference between the waves is and they interfere with each other.
Deduce an expression for the resultant intensity after interference of two sound waves.
What is the frequency of sound, when successive maximum and minimum of a sound were detected at a distance of in a Quincke's tube experiment.( the velocity of sound = )
Describe the method of measuring the speed of sound by Quincke's tube.
Two speakers connected to the same source of fixed frequency are placed apart in a box. A sensitive microphone placed at a distance of from their midpoint along the perpendicular bisector shows a maximum response. The box is slowly rotated until the speakers are in line with the microphone. The distance between the midpoint of the speakers and the microphone remains the same. Exactly five maximum responses are observed in the microphone in doing this. The wavelength of sound wave is (in ):
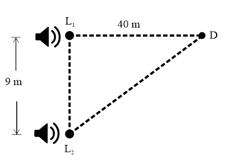
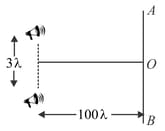
Two loudspeakers and driven by a common oscillator and amplifier are arranged as shown. The frequency of the oscillator is gradually increased from zero and the detector at records a series of maxima and minima. If the speed of sound is , then the frequency at which the first maximum is observed is
An observer receives waves directly from a source of sound distant in a big hall. He also receives waves reflected from the mid-point of high ceiling. The wavelength of sound for constructive interference to take place between two waves, must be
Two speakers connected to the same source of fixed frequency are placed apart in a box. A sensitive microphone placed at a distance of from the mid-point along the perpendicular bisector shows maximum response. The box is slowly rotated till the speakers are in line with the microphone. The distance between the mid-point of the speakers and the microphone remains unchanged. Exactly maximum responses (including the initial and last one) are observed in the microphone in doing this. The wavelength of the sound wave is,
The loudspeakers and driven by a common oscillator and amplifier are set up as shown in the figure. As the frequency of the oscillator increases from zero, the detector at recorded as a series of maximum and minimum signals. What is the frequency at which the first maximum is observed? (Speed of sound )
are two coherent sources of sound having no initial phase difference. The velocity of sound is . No minima will be formed on the line passing through and perpendicular to the line joining if the frequency of both the sources is
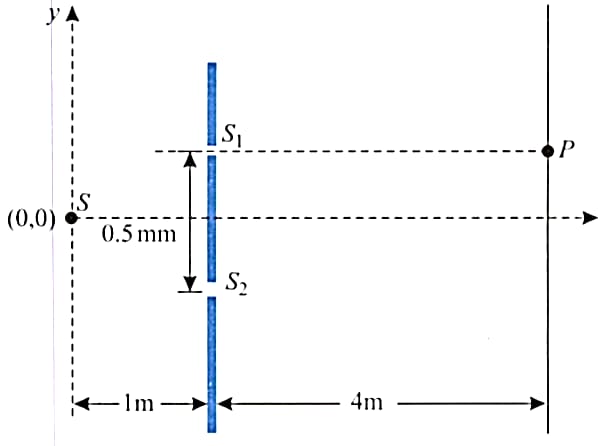
Figure shows a Young’s double slit experiment setup. The source of wavelength oscillates along axis according to the equation , where is in millimeters and is in seconds. The distance between two slits and is .
Statement-1: Two sound waves of equal intensity I produced beats. The maximum intensity of sound produced in beats is 4I.
Statement-2: If two waves of amplitudes and superpose, the maximum amplitude of the resultant wave .
loudspeakers are emitting sound waves of wavelength with an initial phase difference of . At what minimum distance from on line will one hear maxima?
Two periodic waves of intensities and pass through a region at the same time in the same direction. The sum of the maximum and minimum intensities is
Three sources of equal intensities with frequencies and vibrations per second are sounded together. The number of beats per second is
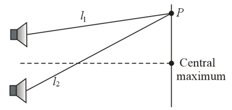
The two loudspeakers in the drawing are producing identical sound waves. The waves spread out and overlap at the point P. This situation is analogous to Young's double-slit experiment, except that sound waves are being used. What is the difference in the two path lengths, if point P is at the third sound intensity minimum from the central sound intensity maximum? Express this difference in terms of the wavelength of the sound.
In Quincke's tube a detector detects minimum intensity. Now one of the tube is displaced by 5 cm. During displacement detector detects maximum intensity 10 times, then finally a minimum intensity (when displacement is complete). The wavelength of sound is :
