Terms in Wave Motion
Terms in Wave Motion: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Phase Lag in Waves, Wave Pulse and Continuous Waves, Terms in Wave Motion, Frequency and Time Period, Amplitude, Angular Frequency, Angular Wave Number, Wave Speed, Particle Speed, etc.
Important Questions on Terms in Wave Motion
The respective displacements (in ) of the two particles are given by the equations:
and these two particles of medium disturbed by the wave propagation are at and , then wave speed is:
Two plane-progressive waves in the same phase must have:
Light waves travel in the form of _____waves.
Progressive waves are waves originating from a source such that they never return to the source.
On an average, a human heart is found to beat times a minute. Its frequency and period are
A point particle is acted upon by a restoring force The time period of oscillation is when the amplitude is The time period for an amplitude will be:
Monochromatic light of frequency travelling in vacuum enters a medium of refractive index . Its wavelength in the medium is
A point particle is acted upon by a restoring force The time period of oscillation is when the amplitude is The time period for an amplitude will be:
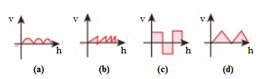
Compare the velocities of the waveforms given below, and choose the correct option.
Two waves meet at a point. The waves have a path difference of The phase difference between the waves is
A particle of mass with velocity at is acted upon by a force . Here, and . The motion is one-dimensional. Then, the speed at which the particle acceleration is zero again, is
A ball is moving uniformly in a circular path of radius with a time period of . If the ball is suddenly stopped at the magnitude of the displacement of the ball with respect to its position at is closest to:
The frequency of tuning fork is and the velocity of sound in air is . The distance travelled by sound while the fork executes oscillations per second is ______.
Transverse waves are generated in two uniform wires and of the same material by attaching their free ends to a vibrating source of frequency . The cross-sectional area of is half that of while the tension on is twice that on . The ratio of the wavelengths of the transverse waves in and is :
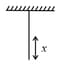
A wire of variable mass per unit length is hanging from the ceiling as shown in figure. The length of wire is . A small transverse disturbance is produced at its lower end. Find the time after which the disturbance will reach to the other ends.
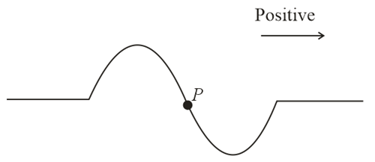
A pulse on a string is shown in the figure. is particle of the string. Then state which of the following is incorrect.
Two sinusoidal waves with same wavelengths and amplitudes travel in opposite directions along a string with a speed If the minimum time interval between two instants when the string is flat is the wavelength of the waves is
For the next two questions
Angular frequency in SHM is given by . Maximum acceleration in SHM is and maximum value of friction between two bodies in contact is , where N is the normal reaction between the bodies.
In the diagram shown, what can be the maximum amplitude of the system so that there is no slipping between any of the blocks ?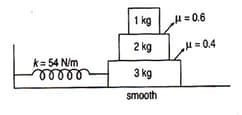
What will be the speed of the transverse wave in a long rope hanging from the ceiling at the upper end and at a point distance from the lower end respectively? Given the mass of the rope is distributed uniformly.
Two steel wires and are such that the diameter of is twice that of and the tension in is half of that in . If transverse waves of same frequency are generated in both the wires, then compute the ratio of velocities of waves in and .
