Principle of Superposition of Waves
Principle of Superposition of Waves: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Superposition of Waves, Principle of Superposition of Waves, Interference of Waves, Interference of Waves on String, Equation of Resultant Wave on String after Interference, etc.
Important Questions on Principle of Superposition of Waves
There is a destructive interference between the two waves of wavelength coming from two different paths at a point. To get maximum sound or constructive interference at that point, the path of one wave is to be increased by
Two plane progressive waves shows destructive interference at point. Which of the following statement is true at point :-
A body is suspended from a string of length and mass . The mass of the body to produce a fundamental mode of frequency in the string is
(Acceleration due to gravity )
The equations of two waves are given by :
These waves are simultaneously passing through a string. The amplitude of the resulting wave is :
Equation of resultant wave on string after interference :-
(iii) Two waves and are interfering one another. What will be the resultant amplitude.
Equation of resultant wave on string after interference :-
(ii) The amplitude of two interfering waves are respectively if the resultant amplitude is . The interference becomes.Equation of resultant wave on string after interference :-
(i) The amplitude of two interfering waves are respectively. The resultant amplitude in case if consructive interference.
Three harmonic waves having equal frequency and same intensity , have phase angles and respectively. When they are superimposed the intensity of the resultant wave is close to:
A travelling wave represented by is superimposed on another wave represented by . The resultant is a
A wave represented by the equation is superposed with another wave to form a stationary wave such that the point is a node. The equation of the other wave is,
An organ pipe open at both ends produces:
The maximum intensity of fringes in Young's experiment is . If one of the slit is closed then, the intensity at that place becomes . Which of the following relations is true?
Three waves of equal frequencies having amplitudes and arrive at a given point with successive phase difference of The amplitude of the resulting wave in is given by,
Two waves are passing through a region in the same direction at the same time. If the equation of these wave are
,
then the amplitude of the resultant wave for is,
Principle of superposition for displacement is valid for :-
Four sources of light waves are represented by :-
Interference fringes may be observed due to superposition of:
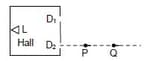
A loudspeaker is placed in the hall with two doors and as shown below. The distance between and is . The loudspeaker is equidistant from and Monotonic sound waves are emitted from the loudspeaker, and it is found that at point which is from and at point the sound intensities are minimum. The line joining and is perpendicular to the line joining and . No other minimum intensity locations can be found between and beyond along the line. What is the frequency of the sound wave generated by the loudspeaker ?(Speed of sound is )
What combination of the following transverse waves will represent a wave travelling along a direction making an angle with the positive and axes
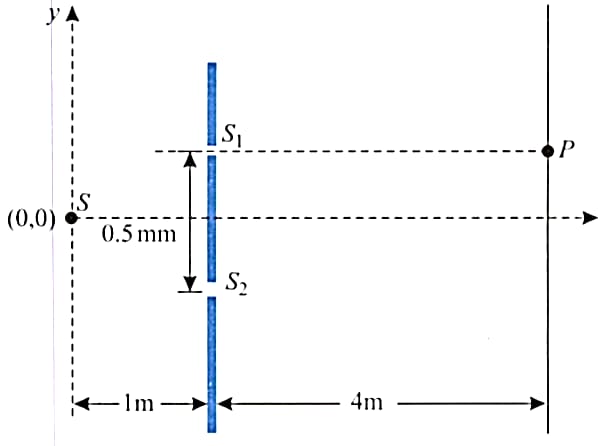
Figure shows a Young’s double slit experiment setup. The source of wavelength oscillates along axis according to the equation , where is in millimeters and is in seconds. The distance between two slits and is .
If the phase difference between two waves of the same frequency is during superposition, then the resultant amplitude is