Lab Activity: Focal Length of a Concave Mirror With Image Distance v and Object Distance u
Lab Activity: Focal Length of a Concave Mirror With Image Distance v and Object Distance u: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Apparatus Used to Find Focal Length of Concave Mirror Using Different Values of v and u, Principle to Find Find Focal Length of Concave Mirror Using Different Values of v and u, Procedure to Find Find Focal Length of Concave Mirror Using Different Values of v and u and Observations Related to Finding Find Focal Length of Concave Mirror Using Different Values of v and u etc.
Important Questions on Lab Activity: Focal Length of a Concave Mirror With Image Distance v and Object Distance u
Which of the following sources of error in a metre bridge experiment to measure the resistivity of a material and the resistance of a specific wire is most likely not to result in an inaccurate measurement?
A metre bridge is balanced with known resistance in the right gap and a metal wire in the left gap. If the metal wire is heated the balance point
A student was performing a meter bridge experiment in a laboratory with a standard resistance and a resistance wire . He found that the balancing length is . Then he replaced by a wire of half the length and half the diameter, those of (of the same material), then the balancing distance (in ) will now be
In a meter bridge experiment, a wire of length and uniform cross-sectional area is used to measure its resistance. The bridge is balanced at a point P where the lengths of the wire on either side are in the ratio . If the known standard resistance is and the length of the wire is L, the resistance of the wire is given by:
What is the principle behind the null point in a meter bridge experiment?
Why is the jockey moved gently from one end to the other during the metre bridge experiment?
In the meter bridge experiment, why is the bridge wire made of a material with a low temperature coefficient?
In the meter bridge experiment, why is it important to ensure that the deflections in the galvanometer are in opposite directions when the jockey is moved along the wire?
As shown, in a lab experiment, a student makes a graph based on his observations. In the u-v graph for a concave mirror, he drew lines OA, AB, and AD. what is the significance of point A?
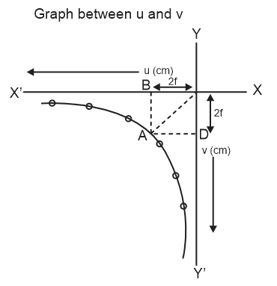
How are the values of and represented at point A on the graph for a concave mirror?
In an experiment of finding focal length of a concave mirror by u-v method, a student prepares following graph of u versus v graph.
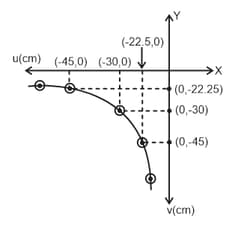
Focal length of mirror is nearly
A concave mirror lab experiment being conducted by a student. What should he adjusted to obtain a clear, sharp image on the screen in front of the concave mirror?
A resistance wire connected in the left gap of the meter bridge balances a resistance in the right gap. This happens at a point where the bridge wire is divided in the ratio of . Assuming the length of the wire to be , calculate the length of the resistance wire?
What will happen to the observed resistance of the wire in a meter bridge experiment if the length of the wire on one side of the jockey is increased while maintaining the same current?
Which of the following stages is not a part of the correct procedure in a meter bridge experiment to find the resistance and resistivity of a wire?
In a meter bridge experiment, the null deflection was obtained at a length of . The known resistance used is . What is the unknown resistance in the wire?
What should be done in a meter bridge experiment to rectify a deflection in one direction indicated by the galvanometer if the null point is not reached?
