Calorimetry
Calorimetry: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Mixing of Liquid and Solid at Different Temperatures, Mixing of Liquid and Vapour at Different Temperatures, Mixing of Liquids at Different Temperatures & Joule's Experiment etc.
Important Questions on Calorimetry
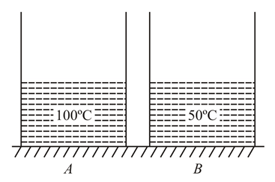
water at and water at is kept in two identical containers and respectively of water equivalent In two independent experiments, if water of container is poured into container the final temperature of mixture is and if water of container is poured into container the final temperature is (heat loss is negligible). Mark the CORRECT option(s).
If ice at water at and steam at are mixed in a container which have negligible heat capacity. [Specific heat of ice specific heat of water then :-
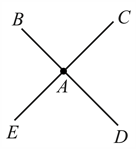
Four identical rods which have thermally insulated lateral surfaces are joined at point . Points are connected to large reservoirs. If heat flows into the junction from point at rate of and from point at inside, flows out from at , which relation(s) is/ are correct for temperature of these points ?
Initially, a beaker has of water at temperature . Later another of water at temperature was poured into the beaker. The temperature, of the water after mixing is
A thermally insulated vessel contains some water at . The vessel is connected to a vacuum pump to pump out water vapour. This results in some water getting frozen. It is given latent heat of vaporization of water at and latent heat of freezing of water . The maximum percentage amount of water that will be solidified in this manner will be:-
Initially, a beaker has of water at temperature . Later another of water at temperature was poured into the beaker. The temperature, of the water after mixing is
Three containers and have water at different temperatures. The table below shows the final temperature when different amounts of water (given in liters) are taken from each container and mixed (assume no loss of heat during the process)
| --- | |||
| --- | |||
| --- | |||
The value of (in to the nearest integer) is .....................
Calorie is the unit of which physical quantity?
Calorie is the unit of which physical quantity?
SI unit of heat is kelvin and SI unit of temperature is joule.
One calorie is nearly equal to _____ .
Find the final temperature in the form of the system when steam at is mixed with ice at Take and the latent heat of fusion and vaporization as and respectively. Find the value of .
A heater supplying constant power watts is switched ON at time to raise the temperature of a liquid kept in a calorimeter of negligible heat capacity. A student records the temperature of the liquid at equal time intervals. A graph is plotted with on the -axis versus on the -axis. Assume that there is no heat loss to the surroundings during heating. Then,
Steam at is passed into of water contained in a calorimeter at till the temperature of water and calorimeter is increased to . The mass of the stean condensed is nearly
(Water equivalent of calorimeter Specific heat of water Latent heat of vapourisation )
An electrically heated coil is immersed in a calorimeter containing of water at . The coil consumes energy at the rate of . The water equivalent of calorimeter & coil is The temperature of water after is-
If of steam at becomes water at which converts of ice at into water at , then the ratio will be,
Two tank and contain water at and respectively. The amount of water that must be taken from and to prepare of water at
Calculate the amount of heat (in calories) required to convert of ice at to steam at
