Thermal Expansion of Solids, Liquids and Gases
Thermal Expansion of Solids, Liquids and Gases: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Thermal Expansion, Thermal Expansion in Solids, Coefficient of Real Expansion & Relation for Volume Expansion etc.
Important Questions on Thermal Expansion of Solids, Liquids and Gases
An aluminium cube of side floats on mercury. The temperature of the system increases from to . Given that the density of aluminium and mercury at are and . while the coefficient of volume expansion of mercury and linear expansion of aluminium are and respectively
An experiment is performed to measure the coefficient of linear expansion of glass.
Experiment: A glass cylinder is filled completely by of mercury at temperature When the temperature of the cylinder is increased upto now it is observed that the cylinder can contain of mercury. In both the cases the temperature of the mercury is assumed to be equal to that of the cylinder. It is known that coefficient of volume expansion of mercury is The coefficient of linear expansion of glass measured from the experiment is
Find the value of
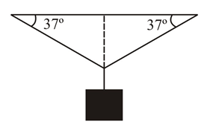
A block is hung by means of two identical wires having cross section area as shown in the diagram. If temperature is lowered by find the mass (in ) to be added to hanging mass such that junction remains at initial position. Given that co-efficient of linear expansion and Young's modulus for the wire.
A wire is made by attaching two segments together end to end. One segment is made of aluminium and the other is steel. The effective coefficient of linear expansion of the two segment wire is . The fraction length of aluminium is then find . (linear coefficients of thermal expansion of aluminium and steel are and respectively)
Strips of steel and brass are fused together as shown in the figure below shown at room temperature. Which of the changes below causes this fused object to attain the shape shown in the figure ? (Physical properties of steel and brass are given in the table)

A vessel is partly filled with a liquid. Coefficient of cubical expansion of material of the vessel and liquid are and respectively. If the system is heated then volume unoccupied by the liquid will necessarily
A simple seconds pendulum is constructed out of a very thin string of thermal coefficient of linear expansion and a heavy particle attached to one end. The free end of the string is suspended from the ceiling of an elevator at rest. The pendulum keeps the correct time at . When the temperature rises to , the elevator operator of mass being a student of physics accelerates the elevator vertically, to have the pendulum's correct time. Find the apparent weight (kg wt) of the operator when the pendulum keeps the correct time at .
A steel metre scale is to be ruled so that the millimetre intervals are accurate to about at a certain temperature. The maximum temperature variation allowed during ruling is (the co-efficient of linear expansion of steel
A metal rod is fixed rigidly at two ends so as to prevent its thermal expansion. If , and respectively denote the length of the rod, coefficient of linear thermal expansion and Young’s modulus of its material, then for an increase in temperature of the rod by , the longitudinal stress developed in the rod is
In which of the following pairs of temperature scales, the size of the degree is identical?
Most matter contracts on heating and expands on cooling (Yes\No).
If the volume of a block metal changes by, when it is heated through , then the coefficient of linear expansion is
Exceptional expansion of water happens below _____ .
Ice is a _____ conductor of heat.
(Choose from the following: good/poor)
A planar frame is made of thin uniform rods. The length of section and is and its coefficient of linear expansion is . The length of section is and its coefficient of linear expansion is . and are of the same length having coefficient of linear expansion . Points and reside on same line, that is, sections and overlap. Then the ratio for which the distance between end and end remains the same at all temperatures is then find the value of .

A liquid having coefficient of volume expansion is filled in a cylindrical glass vessel. Glass has a coefficient of linear expansion of . The liquid along with the container is heated to raise their temperature by . Mass of the container is negligible.
A glass flask of volume one litre at is filled fully with mercury. The flask and mercury are now heated to . How much mercury will spill out ( in ) , if the coefficient of volume expansion of mercury is and linear expansion of glass is respectively?
An iron plate is uniformly heated from to . The change in diameter of a circular hole of diameter is . Find the value of .
The water pipes burst because the water inside them is expanding when it undergoes _____.
_____is an expansion when a solid is heated and there is a change in its volume.
