Cell Division and Continuation of Life
Cell Division and Continuation of Life: Overview
In this topic, we will know the ways and types of cell division, including mitosis and meiosis. It mentions that reproduction leads to the continuation of life. It also illustrates the generation of a new cell from the pre-existing cell.
Important Questions on Cell Division and Continuation of Life
_____ stands for the first growth phase. (Gap 1 or Cap 1)
Mitosis or cell division if known as the _____ stage.
G2 is the time between _____. (H-phase and M-phase/S-phase and M-phase)
_____ phase stands for second growth stage. (Gap 2 or Cap 2)
Which of the following is the shortest phase of M-phase.
The stage in which chromosomes align on the equator of spindle fibre is.
What are the events that occur in the G2 phase?
What are the events that occur in Phase?
Describe the M-phase of cell cycle?
What is M-phase in cell cycle?
Which one of the longest phase of the cell cycle?
What is the G2 phase?
Define G1 phase.
Meiosis I is an equational division in which the number of chromosomes remains constant.
The nuclear membrane in a mitotically dividing cell remains intact up to the metaphase and disappears only in the telophase.
A parent cell divides to form four daughter cells after two consecutive cell divisions with no interphase between them. If each of the four daughter cells has 20 chromosomes enclosed in their nucleus, what will be the number of chromosomes present in the nucleus of the parent cell? (Use numericals)
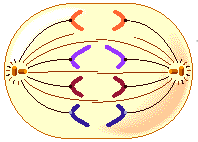
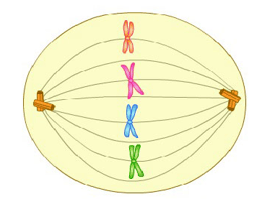
Which phase of mitosis is depicted in the diagram given below?
Which phase of mitosis is shown in the figure given below?
Replication of DNA takes in which phase of the interphase? (Mention the commonly used abbreviation)
_____ is divided into the G1 phase, S phase, and G2 phase.