Structure of a Monocotyledonous Maize Seed
Structure of a Monocotyledonous Maize Seed: Overview
This topic explores the concept of monocotyledonous maize seed. It enhances our knowledge regarding the structure of the monocotyledonous maize seed with the aid of a diagram. It also describes the external and internal structure of monocot seed.
Important Questions on Structure of a Monocotyledonous Maize Seed
Perisperm is
Aleurone layer of seed of maize is specifically rich in:
Give some examples of seeds that show perisperm.
Identify the correct match for the Maize grain from the given options
Perisperm present in the seeds of:
Coleoptile represents
What is persistent nucellus known as and where is it found?
In maize seed, the scutellum is considered cotyledon as it
Which of these are the examples of seeds that show perisperm?
_____ is a nutritive tissue that surrounds the embryo of a seed.
What is ploidy of perisperm?
The sheath enclosing plumule and radicle respectively in monocot seed is:
Some seeds retain a part of endosperm as it is not completely used up during embryo development; while in some seeds, remnants of the nucellus are also persistent. Choose the option with examples of the respective types of seeds.
Perisperm is remnant of
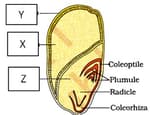
The CORRECT names at 'X', 'Y' & 'Z' respectively are
Observe the diagram given below.
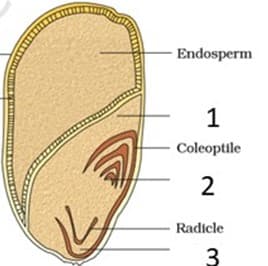
Which of the following describes the parts labeled as and correctly?
i. It represents the plumule which further develops into the shoot.
ii. Large shield-shaped cotyledon.
iii. Further develops into the primary root.
The persistent nucellus is a
Identify the correct statements about the angiospermic embryo.
i. The scutellum is centrally placed in monocots.
ii. Plumule is the stem tip and radicle is the root tip in dicots.
iii. Coleorrhiza is part of the hypocotyl in monocots.
iv. Monocotyledonous zygote gives rise to a globular heart-shaped embryo.
Perisperm is:
Aleurone grains are rich in