Transportation in Humans
Transportation in Humans: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Circulatory System in Human Beings, Role of Blood in Circulation, Human Heart, Chambers of Heart, Atria, Ventricles, Heart Valves, Vena Cava, Aorta, Pulmonary Arteries, Pulmonary Veins, Working of a Human Heart, Double Circulation, Pulmonary Circulation, Systemic Circulation, Blood Pressure, Systolic Pressure, Diastolic Pressure, Sphygmomanometer, Blood Vessels, Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, Components of Blood, Red Blood Corpuscles, Blood Clotting, Lymph, Lymph Vessels, Electrocardiogram, P-wave in Electrocardiogram, QRS complex in Electrocardiogram, T-wave in Electrocardiogram, ECG Axis Deviation & Electrocardiograph (ECG) etc.
Important Questions on Transportation in Humans
Where in do the pulmonary veins open?
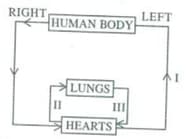
Figure below reflects the blood circulation system in the human body. Which of the path contains oxygenated blood.
Blood pressure is measured by an instrument called:-
Which of the following is the body's largest blood vessel
Which of the following cellular component blood containing haemoglobin
The following statements about blood vessels is/are correct.
(A) Arteries have thin and less muscular walls
(B) Walls of veins are non-elastic
(C) Arteries have no valves in their inner lining
(D) Veins do not collapse when empty
Separation of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood.
I. Fulfils energy requirement of the body.
II. Ensures the effect transfer of oxygen in the body.
Oxygen rich blood from lungs comes to which chamber of the heart-
The correct statement which explains the structure of veins is :
Blood cells are manufactured in our:
Choose correct statement for human:
Mineral ion associated with haemoglobin is
What helps to store oxygen in our muscles?
Which one helps in blood clotting?
Which of the metallic ions is essential for blood clotting?
In humans, the prothrombin required for blood clotting is produced in
Blood clot inside a blood vessel is known as
