The Gas Laws
The Gas Laws: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Gas Laws, Boyle's Law, Graphs Based on Boyle's Law, Charles' Law, Graphs Based on Charles' Law, Absolute Zero Temperature, Gay-Lussac's Law, Graphs Based on Gay-Lussac's Law, Avogadro's Law, Ideal Gas, Combined Gas law, Ideal Gas Equation, Universal Gas Constant, Calculation of Universal Gas Constant, Density and Molar Mass Relation & Average Speed etc.
Important Questions on The Gas Laws
What volume of oxygen gas measured at and 1 atm, is needed to burn completely 1L of propane gas measured under the same conditions?
In a closed flask of 5 litres, 1.0 g of is heated from 300 K to 600 K. Which statement is not correct?
A bubble of air is underwater at temperature and the pressure 1.5 bar. If the bubble rises to the surface where the temperature is and the pressure is 1.0 bar, what will happen to the volume of the bubble?
By what factor does the average velocity of a gaseous molecule increase when the temperature (in Kelvin) is doubled ?
Cyclopropane and oxygen at partial pressures torr and torr respectively are mixed in a gas cylinder. What is the ratio of the number of moles of cyclopropane to the number of moles of oxygen (Assume no reaction).
The correct value of the gas constant is close to:
If are pressure, volume, molar mass, temperature and gas constant respectively, then for an ideal gas, the density is given by
If are pressure, volume, molar mass, temperature and gas constant respectively, then for an ideal gas, the density is given by
Arrange the following relevant points in a proper sequence for explaining why Kelvin scale is preferred to Celsius scale in the study of gases.
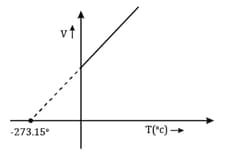
- is the least possible temperature.
- A graph of volume vs temperature is a straight line passing through origin.
- A graph of volume vs temperature is a straight line which intersects volume axis at some point.
- Extrapolation of straight line touches the volume axis at.
- is called absolute zero or .
- All values of temperature are positive in Kelvin scale.
- Usage of negative values for temperature gives negative values for other properties like pressure and volume.
At constant temperature, a gas is at a pressure of . At what pressure, its volume decreases by ?
For which of the following reactions, is Gay-Lussac's law is not applicable?
Which of the following graphs is true for the given mass a gas at constant temperature?
At constant temperature, when the volume of a gas is reduced to , the pressure will increase _____.
Which of the following graphs is true for a given mass of a gas at constant pressure?
Which of the following graphs is true for the given mass a gas at constant temperature?
Which amongst the following options is correct graphical representation of Boyle's Law?
A fixed mass of an ideal gas is maintained at constant volume. The pressure of the gas at the triple point of water is . What is the thermodynamic temperature of the gas when its pressure is ?
Which of the following relation is correct for fixed number moles of gas at constant temperature?
A mixture if hydrogen and oxygeb hs volume , temperature , pressure and mass .Calculate the masses of hydrogen and oxygen in the mixture.
At constant pressure following graph represents