Versatile Nature of Carbon
Versatile Nature of Carbon: Overview
This topic explains that carbon has a high tendency for catenation due to strong covalent bonding. Saturated and unsaturated carbon compounds possess single and multiple bonds, respectively. Assigning names to an organic compound based on certain rules is called nomenclature.
Important Questions on Versatile Nature of Carbon
Name the following compound and write its chemical formula.
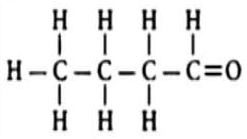
Define organic and inorganic compounds.
Write the molecular formula and structural formula for pentane.
Write the molecular formula and structural formula for cyclohexane.
Write any two differences between saturated and unsaturated carbon compounds.
The general formula for homologous series of haloalkanes is _____.
(Enter your correct answer as )
Haloalkanes are derived from the general formula .
The general formula for homologous series of haloalkanes is:
What is the homologous series of haloalkanes?
The correct parent chain for the following compound is:
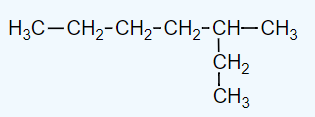
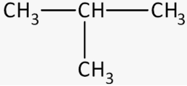
The parent chain for isopropyl alcohol contains carbon atoms.
The parent carbon chain for the following compound is _____.
The chemical formula of hexane is .
The chemical formula of hexane is _____.
(Enter your correct answer as )
What is the formula of hexane?
Draw and explain the chain structure of n-hexane.
What prefix is used to name a hydrocarbon with two carbon atoms?
The prefix for the alkyl group containing seven carbons is _____.
Primary prefix is used to indicate whether the molecule is cyclic or not.
Write the formulae and names of first three carboxylic acids.
