Versatile nature of carbon
Versatile nature of carbon: Overview
This topic explains that carbon has a high tendency for catenation due to strong covalent bonding. Saturated and unsaturated carbon compounds possess single and multiple bonds, respectively. Assigning names to an organic compound based on certain rules is called nomenclature.
Important Questions on Versatile nature of carbon
The property of an element to bond with itself through covalent bonds to form a chain or ring is called:
An element, other than carbon, which exhibits the property of catenation up to seven or eight atoms is _____.
Diamond and graphite show different physical properties, although they are made up of carbon.
This relationship between diamond and graphite is called _____.
While cooking, if the bottom of the vessel is getting blackened on the outside, it means that
The molecular formula of alcohol which can be derived from butane is
Which of the followoing formula represents a saturated hydrocarbon?
Buckminsterfullerene is an allotropic form of
The existence of an element in more than one form and each form has different physical properties but identical chemical properties are called _____.
Out of sodium chloride(NaCl) and methyl chloride(CH3Cl), melting and boiling point of NaCl are _____ than CH3Cl.
Which of the following statements are correct for covalent compounds?
The unsaturated hydrocarbons which contain one or more triple bonds are called _____.
The unsaturated hydrocarbons which contain one or more double bonds are called _____.
Which of the following formula represents a saturated hydrocarbon?
The earth's crust has only _____% carbon in the form of minerals.
Compounds of carbon having double or triple bonds between their carbon atoms are called _____ compounds.
Compounds of carbon, which are linked by only single bonds between the carbon atoms are called _____ compounds.
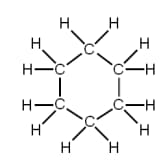
The name of the hydrocarbon shown above is _____.
Identify the correct structural formula of benzene.
The valency of a carbon atom is _____.
Which of the following is an example of an inorganic compound?
