Alkanes
Alkanes: Overview
In this topic, we will learn in detail about the nomenclature, isomerism, preparation and physical and chemical properties of alkanes. It explains substitution reactions, combustion, controlled oxidation and conformations.
Important Questions on Alkanes
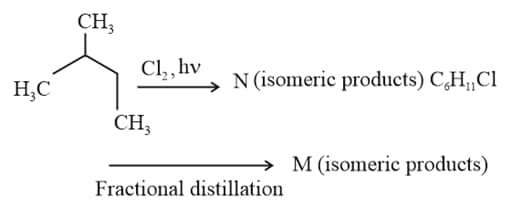
contains X number of allylic hydrogen and contains Y number of allylic hydrogen.The number of structural isomers of are
The increasing order of reduction of alkyl halides with zinc chloride and dil.HCl is
Identify the molecular formula of simple alkane that formed by the reaction between sodium acetate and soda lime
Alkane can not be obtained using zinc and hydrochloric acid from:
Complete the following equation:
Enter your correct answer as , , or .
Write the chemical equation for burning of methane.
Why is ethane insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents?
Ethane is easily soluble in water but insoluble in benzene.
Methane has a low melting point and boiling point, give a reason for it.
The boiling point of methane is _____ (approximately).
The melting point and boiling point of methane is very low.
Ethane can be prepared in the laboratory by decarboxylation of the sodium salt of fatty acid.
How ethane can be prepared in the laboratory? Write the chemical equation for it.
The structure of a methane molecule is tetrahedral and contains four covalent bonds.
Complete the following equation:
_____
Enter your correct answer as , , or .
Methane is prepared in the laboratory by heating a mixture of sodium acetate with soda ash.
Write the balanced equation for the laboratory preparation of methane.