Electric Current and Circuit
Electric Current and Circuit: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Electric Current, Unit of Current, Electric Cell, Terminals of an Electric Cell, Basic Components of a Battery, Electromotive Force, Internal Resistances of Cell, Source of Electricity in an Electric Cell, Production of Electric Current in a Cell, Direction of Flow of Current outside a Cell, Direction of Flow of Current inside a Cell, Analogy of Electric Current with Water Flow, Conventional Direction of Electric Current, Current through a Conductor, Flow of Charge through Wire, Potential Difference across Terminals of Battery Getting Discharged & Uses of Electric Cells etc.
Important Questions on Electric Current and Circuit
A copper rod of cross-sectional area carries a uniform current through it. At temperature , if the volume charge density of the rod is , how long will the charges take to travel a distance ?
In a current carrying conductor the motion of an electron is
In an electric bulb filament, current is passed for . Calculate the electric charge passing through the circuit.
A current of is drawn by a filament of and electric bulb for minutes. The number of electrons flowing through the circuit are
In a conducting wire, charge flows in . The current flowing in the conductor is :
An electric lamp is marked 60 W. 240 V. If it operates at 200 V, the current through it will be
The wire having a black plastic covering is a
The wire having a red plastic covering is a
Electricians use rubber gloves while working because
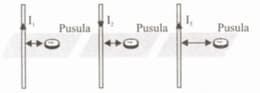
Since the deflection amounts of the identical compasses found as shown above in the figure on the sides of the wires in the same medium over which I1, I2 and I3, currents pass are equal, what is the relationship between the currents?
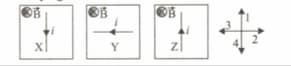
Wire X, Y and Z are lying in the same magnetic fields. As per information in the diagram predict the direction of force experiment by current carrying wire.
When the currents in the figure pass through the flexible K and L wires, what is the position of the wires?

The force between two parallel wires carrying current has been used to define
Conventionally, the direction of the current is taken as
If I is the current through a wire and e is the charge of electron, then the number of electrons in t seconds will be given by
