Newton's Laws of Motion
Newton's Laws of Motion: Overview
In this topic, we will study Newton's laws of motion along with its applications and importance in physics. It also explains how to solve numerical problems based on Newton’s first, second and third laws with the aid of solved examples.
Important Questions on Newton's Laws of Motion
A particle of mass m is moving with a uniform velocity It is given an impulse such that its velocity becomes The impulse is equal to :
A particle of mass m is moving with a uniform velocity It is given an impulse such that its velocity becomes The impulse is equal to :
A large force is acting on a body for a short time. The impulse imparted is equal to the change in _____.
Force is one _____ if a mass of one kilogram gets an acceleration of .
A player caught a cricket ball of mass moving at a rate of . If the catching process is completed in , the force of the blow exerted by the ball on the hand of the player is equal to
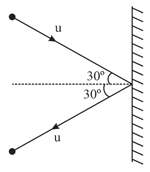
A ball of mass strikes a rigid wall with speed at an angle of with the normal and gets reflected with the same speed and at the same angle, as shown in the figure. If the ball is in contact with the wall for time , then the force experienced by the wall is:
A block of the mass of is moving on the -axis. A force acting on the block is shown. The velocity of the block at time is . What is the speed of the block at time ?
A particle of mass is moving with a uniform velocity . It is given an impulse such that its velocity becomes . The impulse is equal to
A ball of mass is moving towards a batsman at a speed . The batsman strikes the ball and deflects it by an angle , without changing its speed. The impulse to the ball is given by
At time second, a particle of mass 3 kg has position vector metre, where The impulse of the force during the time interval is -
A ball of mass strikes a wedge of mass horizontally with a velocity of . Just after collision, velocity of wedge becomes . Friction is absent everywhere and collision is elastic. Select the correct alternative.
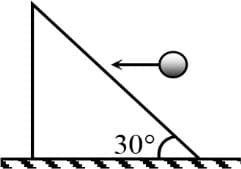
A particle of mass kg moving towards the wall of a vessel at a velocity of strikes it at an angle of to the normal and rebounds at the same angle at the same speed. The impulse of the force experienced by the wall during the impact is -
Three stationary particles of masses and are under the action of same constant force for the same time. If , the variation of momentum of particles with time for each will be correctly shown as
A golf ball of mass 0.05 kg placed on a tee, is struck by a golf club. The speed of the golf ball as it leaves the tee is , the time of contact between them is 0.02 s. If the force decreases to zero linearly with time, then the average force during the contact is
A ball of mass is thrown normally against a wall with a speed of . It rebounds normally with a speed of . The impulse of the force by the ball on the wall is
Consider the following statement. When jumping from some height, you should bend your knees as you come to rest instead of keeping your legs stiff. Which of the following relations can be useful in explaining the statement?
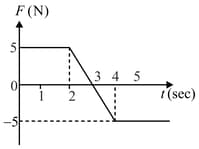
A particle of mass 2 kg is initially at rest. A force acts on it whose magnitude changes with time. The force- time graph is shown below
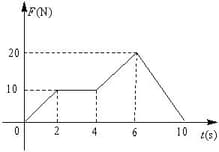
The velocity of the particle after 10 s is
Two particles of masses and in projectile motion have velocities and respectively at time . They collide at time . Their velocities become and at time while still moving in air. The value of
is
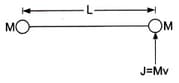
Consider a body, shown in diagram, consisting of two identical balls, each of mass connected by a light rigid rod. If an impulse is imparted to the body at one of its ends, what would be its angular velocity?