Gravitational Potential Energy and Motion of Satellite
Gravitational Potential Energy and Motion of Satellite: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Gravitational Potential, Gravitational Potential Energy, Gravitational Potential Energy and Mgh, Motion of Satellites, Path of Satellites, Weightlessness in Satellites, Orbital Speed of Satellites, Orbital Time Period of Satellites, Geostationary Satellites, Geostationary Orbits, Application of Geostationary Satellites & Projection Speed and Trajectory of Satellites etc.
Important Questions on Gravitational Potential Energy and Motion of Satellite
A satellite revolves in the geostationary orbit but in a direction east to west. The time interval between its successive passing about a point on the equator is
Why do we put negative sign in formula ?
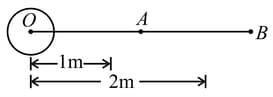
A sphere of radius and mass has a uniform mass distribution. A mass of is moved from a point to as shown in fig. The amount of work done is
A rod of mass and length is placed along the axis of ring of mass and radius . The centres of ring and rod coinciding initially. If rod is fixed and ring is given velocity along the rod, then find velocity of ring when it reaches the end of rod (Consider the mutual gravitation force only)
A satellite is launched into a circular orbit above the surface of the earth. Find the period of revolution in nearest integer (in hours) if the radius of the earth is and the acceleration due to gravity is (Take and ).
For a satellite projected from the Earth's surface with a velocity greater than the orbital velocity, the nature of the path it takes when its energy is negative, zero and positive respectively is.
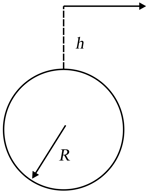
A particle is taken to a height from earth's surface and is projected with a velocity as shown. Assume . Choose the correct alternative
What are the applications of geostationary satelllites?
Why is geostationary orbit at the equator?
The satellite travels along the _____ path and never returns to the point of projection, When .
The nature of the path of the satellite depends upon
State the conditions for various possible orbits of satellite depending upon the horizontal speed of projection.
Gravitational potential energy is expressed mathematically as _____.
Calculate the gravitational potential energy of a body of mass and is above the ground.
Astronauts inside spaceship feel zero weight.
Weightlessness in satellite is due to
List any two characteristics of a geostationary satellite.
The period of a satellite in a circular orbit around a planet is independent of
Define time period of a satellite.
Which of the following is the expression for orbital velocity of a satellite in a circular orbit.
