Image Formation by Lenses
Image Formation by Lenses: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as image formation by a lens, images formed by convex lens for different positions of an object, important rays for image formation in lens, sign convention for spherical lenses, and lens formula.
Important Questions on Image Formation by Lenses
An object of height is placed at from a concave lens of focal length . Select the correct size of the image.
An object is placed at a distance from a convex lens of focal length . Select the correct image distance and nature of the image.
The convex lens always gives small virtual image.
The power of lens depends on the focal length of the lens.
Assertion: Virtual images are always erect.
Reason: Virtual images are formed by diverging lenses only.
The image distance in the mirror formula is normally written by the letter .
What would be the image distance of an object when it is kept on the principal axis at a distance of in front of a concave mirror having the focal length of ?
The image distance of an object when it is kept on the principal axis at a distance of in front of a concave mirror having the radius of curvature is approximately .
A _____ (convex / concave) lens can produce both real and virtual images.
At what distance from a convex lens of focal length , should an object be placed so that the lens forms an image of the same size as the object?
To obtain a magnification of, with a convex lens, the object should be placed:
You are given two convex lenses and made of the same glass. is thicker than . Choose the correct answer from the following.
Out of the five incident rays shown in the figure find the two rays that are obeying the laws of refraction and may be used for locating the position of image formed by a convex lens__
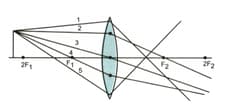
When the object is placed between the and of a convex lens, it produces a virtual, erect and magnified image.
Which of the following statements is true?
Select the correct ray diagram for image formation by concave lens when the object is placed between infinity and optical centre.
Identify from the following the correct statement about the characteristics of the image formed by a convex lens having a focal length of when the object is kept on the principal axis at a distance of and .
A doctor has prescribed a corrective lens of power . Find the focal length of the lens in meter. (round off up to two decimal places)
Select the correct ray diagram for the image formation in a convex lens when an object is placed beyond .
