Refractive Index
Refractive Index: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Snell's Law, Absolute Refractive Index & Relative Refractive Index etc.
Important Questions on Refractive Index
rays, which are initially sent parallel to each other, follow the path in the figure as they pass through K, L and M environments.
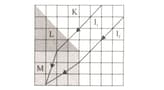
So, what is the relationship between the refractive indices of the media?
(Partitions are equally spaced)
The light beam I reaches point P by passing through K, L and M transparent environments with vertical cross-sections as in the figure.
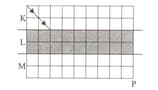
Since the refractive indices of K, L and M environments are respectively for the relationship between them;
Which of following statements could be correct?
(Partitions are evenly spaced.)
I.
II
III.
The I beam follows the path in the figure in parallel K, L and M medium.
Accordingly, in order for the I beam to pass into M medium.
|. Increasing the refractive index of M medium
||. Reducing the refractive index of L media.
|||. Increasing the angle
Which of the action can be done alone?
The path of a monochrome I light beam in X,Y and Z transparent media is as shown in the figure.
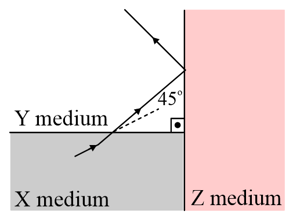
What is the relationship between the refractive indices of the X, Y and Z medium?
The I beam, which is a mixture of red, green and blue colours,is refracted from the glass medium to the O-centered air environment as shown in the figure.
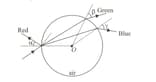
So what is the relationship between angles ?
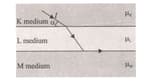
The path followed by the I light beam in K, L and M transparent medium with refractive indices is as in the figure given below.
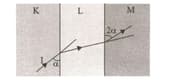
So, what is the relationship between the refractive indices My. H, and My of the media?
The paths of the rays coming from K. medium to L and M medium are as in the figure.
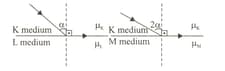
What is the relationship between the refractive indices of the K, L and M environments?
Spherical Y medium with centre O is one side X and the other side is Z environment. The I beam coming to the intersection surface of the X medium and the Y medium passes as an I beam to the Z medium as a result of the refractions.
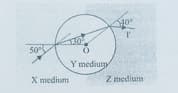
Accordingly, what is the relationship between the sizes of the refractive indices of the X,Y and Z medium ?
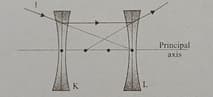
The path of incident ray falling on the system of two concave lens with common Principle axis as shown in the diagram. What is the ratio of if all dots are equally placed.
Same lens is placed in three different medium namely K,L and M. If represents the refractive indices. Choose the appropriate option on the basis of the information in the diagram.

Mark True or False.
1. If angle of refraction is smaller than the angle of incidence then medium of refraction is optically denser but it may have less density than that of medium of incidence.
2. If refractive index of medium is n then speed of light is n times the speed of light in vacuum.
3.
4. If I am standing near a pond then fish in the pond finds my height taller than my actual height.
Choose the appropriate option:
A parallel beam of light falls at an angle to interface of two mediums whose refractive indices are and it has speed in two mediums then
Which of following statement/relation is/are correct?
1. represents refractive index of medium.
2. Refractive index of a medium is a number associated with the ratio of speed of light in it to the speed of light in vacuum.
3.
4. , where n1, n2 are the frequencies of wave in two medium.
Mark True or False.
1. When light travels from one medium to other its speed depends upon the density of medium.
2. When light travels from one medium to other frequency of light wave is invariant.
3. Sound wave also suffers the same laws of refraction like a light wave.
4. Speed of light wave does not change when it enters normal to the interface of two medium.
Choose the appropriate option:
If rectangular slab of refractive index is placed over a coin lying on table. What is value of ? If the coin appear to be raised by 1/3 of real depth.
A glass prism of refractive index 1.5 is immersed in kerosene (). A light beam incident normally on the face AB is totally reflected to reach the face BC if
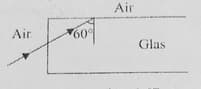
A light ray from air is incident (as shown in figure) at one end of glass fiber ( refractive index ) making an incidence angle of on the lateral surface, so that it undergoes a total internal reflection. How much time would it take traverse the straight fiber of length 1 km?
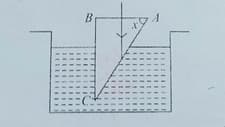
A coin is kept at bottom of an empty breaker. A travelling microscope is focused on the coin from top, now water is poured in beaker up to a height of 20 cm. By what distance and in which direction should the microscope be moved to bring the coin again in focus
A rectangular slab of refractive index is placed over another slab of refractive index 3, both slabs being identical in dimensions . If a coin is placed below the lower slab, for what value of will the coin appear to be placed at the interface between the slabs when viewed from the top
A ray of light passes from vacuum into a medium of refractive index , the angle of incidence is found to be twice the angle of refraction . If angle of incidence is very small then of medium is
