Galvanometer
Galvanometer: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Galvanometer, Construction of Moving Coil Galvanometer, Working Principle of Moving Coil Galvanometer & Sensitivity of Galvanometer etc.
Important Questions on Galvanometer
Statement -1: The sensitivity of a moving coil galvanometer is increased by placing a suitable magnetic materials as a core inside the coil.
Statement -2: Soft iron has a high magnetic permeability and cannot be easily magnetized or demagnetized.
In a moving coil galvanometer, the torque on the coil can be expressed as , where is the current through the wire and is a constant. The rectangular coil of the galvanometer having number of turns , area , and moment of inertia , is placed in magnetic field . Find the torsional constant of the spring, if a current produces a deflection of in the coil in reaching the equilibrium position.
A moving coil galvanometer on connecting with a high resistance in series is converted into:
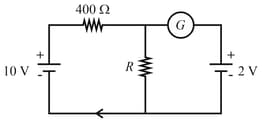
If the galvanometer does not show any deflection in the circuit shown, the value of is given by:
The current sensitivity of moving coil galvanometer is increased by . This increase is achieved only changing in the number of turns of coils and area of cross section of the wire while keeping the resistance of galvanometer coil constant. The percentage change in the voltage sensitivity will be:
Given below are two statements:
Statement I: If the number of turns in the coil of a moving coil galvanometer is doubled then the current sensitivity becomes double.
Statement II: Increasing current sensitivity of a moving coil galvanometer by only increasing the number of turns in the coil will also increase its voltage sensitivity in the same ratio
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
In a moving coil galvanometer, if number of turns increases by , then change in voltage sensitivity is
In a moving coil galvanometer, when the number of turns of the coil is doubled,
The current sensitivity of a moving coil galvanometer increases by when its resistance is doubled. Calculate, by what factor does the voltage sensitivity change?
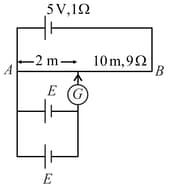
In the given figure, if galvanometer shows null deflection then emf of each cell will be
In order to increase the current sensitivity of a moving coil galvanometer the
A galvanometer having a coil resistance of gives a full-scale deflection, when a current of is passed through it. The value of the resistance, which can convert this galvanometer into an ammeter giving a full scale deflection for a current of , is:
In order to increase the sensitivity of galvanometer,
The thermo e.m.f of the copper-constantan couple is per degree. The smallest temperature difference that can be detected with this couple and a galvanometer of resistance capable of measuring the minimum current of is:
In a Radial Magnetic field:
Phosphor-bronze strip in a suspended coil galvanometer is used as a suspension fibre :
The maximum current in a galvanometer can be . It's resistance is . To convert it into an ammeter of , a resistor should be connected in
When a galvanometer is shunted with a resistance, the deflection is reduced to one-fifth. If the galvanometer is further shunted with a wire, find the ratio of decrease in current to the previous current (the main current remains the same).
Two galvanometers A and B requires and current, respectively to produce the same deflection of division. Then
Two moving coil galvanometers, and have coils with resistances and , cross-sectional areas and , number of turns and respectively. They are placed in magnetic fields of and respectively. Then the ratio of their current sensitivities and the ratio of their voltage sensitivities are respectively.
