Applications of Newton's Laws of Motion
Applications of Newton's Laws of Motion: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Rocket Propulsion, Variable Mass System, Motion on Inclined Plane, Limitations of Newton's Laws of Motion, Motion of Connected Bodies, Theory of Rocket Propulsion and, Motion of Blocks Connected by a String
Important Questions on Applications of Newton's Laws of Motion
Choose the principle behind the rocket propulsion from the following options:
Explain rocket propulsion on the basis of law of conservation of linear momentum and Newton's third law of motion.
If a body changes in both velocity and mass with respect to time. Then the force acting on it is
State Newton's second law of motion. Under what conditions does it take the form F=ma?
The apparent weight of a body in an elevator moving with downward acceleration is greater than that of the actual weight of a body.
What happens to the weight of a person when lift goes down with some acceleration.
What will happen to a person's weight when he is in a moving in a lift of constant speed?
What will happen to a person's weight, when he is moving in a lift with a constant speed?
Choose the correct equation from the following options.
Derive the velocity of rocket as a function of time.
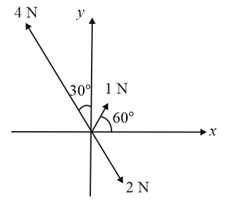
Three forces acting on a body are shown in the figure. To have a resultant force only along the , the magnitude of the minimum additional force needed is:
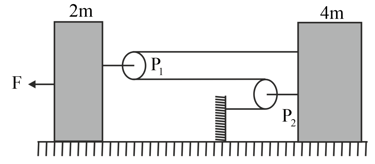
Calculate the acceleration of the block B in the figure, assuming the surfaces and the pulleys and are all smooth and pulleys and string are light. (take )
A block of mass is placed on a smooth wedge of inclination The whole system is accelerated horizontally so that the block does not slip on the wedge. The force exerted by the wedge on the block ( is acceleration due to gravity) will be
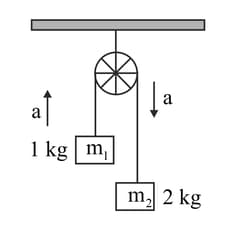
Two masses are connected by a light inextensible string and suspended using a weightless pulley as shown in the figure. Assuming that both the masses start from rest, the acceleration of the centre of mass is _____ .(Take )
Three Forces F1, F2, and F3 together keep a body in equilibrium. If F1 = 3 N along the positive X- axis, F2 = 4N along the positive Y-axis ,then the third force F3 is
A man of mass is riding in a lift .The weights of the man, when the lift is accelerating upwards and downwards at are respectively?
A body is moving under the action of two forces . For its velocity to become uniform a third force acts on it, then this force can be given by:
If momentum of a body remains constant, then mass-speed graph of body is
A block of mass is resting on a smooth horizontal surface. One end of a uniform rope of mass is fixed to the block, which is pulled in the horizontal direction by applying force at the other end. The tension in the middle of the rope is
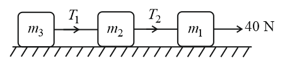
Three blocks of masses, and are connected by a massless string as shown in the figure on a frictionless table. They are pulled with a force of . If and , then, the tension will be,