Dispersion of Light
Dispersion of Light: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Dispersion, Dispersion of White Light, Spectrum of White Light, Rainbow, Colours of Rainbow, and Refraction through a Prism.
Important Questions on Dispersion of Light
The change in speed causes the light to change direction and bend.
What does refraction through the prism mean?
Explain the refraction of light through a prism with the help of a diagram.
Rainbow is a natural phenomenon that is formed due to the dispersion of light.
Fill half a bowl with water. Now place the mirror strip in the bowl as shown in the picture. Now keep it facing the sun so that the sun rays fall on the mirror strip. The light reflected by the mirror should now reflect on a white wall.
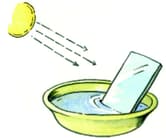
What can you see on the wall?
Fill half a bowl with water. Now place the mirror strip in the bowl as shown in the picture. Now keep it facing the sun so that the sun rays fall on the mirror strip. The light reflected by the mirror should now reflect on a white wall.
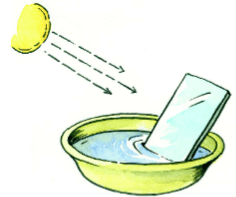
What colours can you see on the wall? Find out the order of the colours and draw its picture.
How many colours are there in a rainbow?
The wavelength of red light is _____.
Any light that gives a spectrum similar to that of sunlight is called _____.
Splitting of white light into seven colours on passing through the glass prism is called _____.
_____the speed of light in the glass prism, makes the light bend more.
A prism ABC (with BC as base) is placed in different orientations. A narrow beam of white light is incident on the prism as shown in figure. In which of the following cases, after dispersion, the third colour from the top corresponds to the colour of the sky?
_____ is caused by dispersion of sunlight by tiny water droplets, suspended in the atmosphere after a rainfall.
List the three phenomena of light responsible for the formation of the rainbow in the sky.
The refractive index assumes entrance of light from a _______.
White light is a mixture of_______.
Read the passage and answer the questions below.
We know that the white light is actually a combination of seven different colours of light. These are violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange and red. All these colours together are called a natural spectrum. A natural spectrum is formed when light scatters at different wavelengths in the atmosphere. These colours are clearly visible when a rainbow is formed. So, if there are seven colours in white light, why does the sky appear mostly blue? Let us understand the reason behind this. Light travels in the form of waves. Blue light has a short wavelength and red light has a long wavelength.
An English physicist, John William Strutt Lord Rayleigh() explained that lights of different wavelengths get scattered when they hit the molecules of hydrogen and oxygen in the atmosphere. Owing to its shorter wavelength, the blue-coloured light gets scattered more than the red one. As such the sky appears blue.
Name the scientist who explained the reason behind the blue colour of the sky.Read the passage and answer the questions below.
We know that the white light is actually a combination of seven different colours of light. These are violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange and red. All these colours together are called a natural spectrum. A natural spectrum is formed when light scatters at different wavelengths in the atmosphere. These colours are clearly visible when a rainbow is formed. So, if there are seven colours in white light, why does the sky appear mostly blue? Let us understand the reason behind this. Light travels in the form of waves. Blue light has a short wavelength and red light has a long wavelength.
An English physicist, John William Strutt Lord Rayleigh(1842-1919) explained that lights of different wavelengths get scattered when they hit the molecules of hydrogen and oxygen in the atmosphere. Owing to its shorter wavelength, the blue-coloured light gets scattered more than the red one. As such the sky appears blue.
Why does the sky appear blue?Read the passage and answer the questions below.
We know that the white light is actually a combination of seven different colours of light. These are violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange and red. All these colours together are called a natural spectrum. A natural spectrum is formed when light scatters at different wavelengths in the atmosphere. These colours are clearly visible when a rainbow is formed. So, if there are seven colours in white light, why does the sky appear mostly blue? Let us understand the reason behind this. Light travels in the form of waves. Blue light has a short wavelength and red light has a long wavelength.
An English physicist, John William Strutt Lord Rayleigh(1842-1919) explained that lights of different wavelengths get scattered when they hit the molecules of hydrogen and oxygen in the atmosphere. Owing to its shorter wavelength, the blue-coloured light gets scattered more than the red one. As such the sky appears blue.
Name the natural spectrum. How it is formed?Sunlight is made up of _____ colours.
