Refraction of Light
Refraction of Light: Overview
This topic explains the refraction phenomenon, when a ray of light passes from one optical medium to another medium and deviates. Snell’s Law of Refraction states that the ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is constant.
Important Questions on Refraction of Light
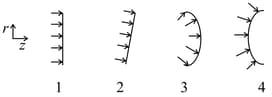
The refractive index of certain material is given by where represents density of the material such that and is a constant. A planar wavefront of light propagating along direction enters this material from left whereas the density of the material increases in the radial distance in the plane perpendicular to the propagation axis. Select the wavefront that correctly describes the propagation of light in this medium.
The value of angle of deviation of a parallel glass slab is .
What is the value of angle of deviation of a parallel glass slab?
The angle of incidence of a plane wavefront is on the surface of the glass. The angle of deviation would be if the angle of refraction is
A plane wavefront is incident at an angle of on the surface of the glass. Calculate the angle of deviation if the angle of refraction is
The I beam. which is sent parallel to the principal axis to the optical system formed by convergent lenses K and L with coincident principal axes, emerges from the apparatus as an I' beam parallel to the principal axis as a result of refractions,
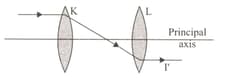
According to this,
I. Shifting lenses K and L evenly in the same direction
IL. Moving K lens closer to L lens
ill. Approximation of the 1 beam to the principal axis while keeping it parallel to the principal axis
Which one of the operations results in the I' beam coming out of the setup again parallel to the principal axis?
The I light beam follows the path in the figure in the arrangement formed in X, Y and Z transparent media.
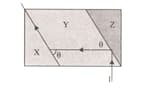
Since the refractive indices of the X, Y and Z environments are respectively,
what is the relationship between them?
The path of a monochrome I beam in parallel K, L and M transparent media is as shown in the figure.
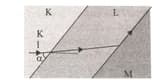
Accordingly in order for the I beam to reflect fully at the interface of L medium to M medium:
|. Angle should be increased
||. Refractive index of L medium should be increased
|||. Refractive index of M medium should be reduced
Which of the procedures can be done?
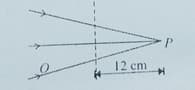
In figure given below, a beam of light converging at point P. When a concave lens of focal length 16 cm is introduced in the path of the beam at a place shown by dotted line the beam converges at a distance x from the lens. The value of x will be equal to
Velocity of light in medium 1 is and in medium 2 is . The refractive index of medium 1 with respect to medium 2 is
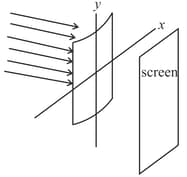
Consider a plane parallel beam of light incident on a plano-cylindrical lens as shown below. Which of the following will you observe on a screen placed at the focal plane of the lens?
If a swimmer inside water looks at an aeroplane in the sky, then which of the following conditions are fulfilled?
Second law of refraction states that the ratio of cosine of angle of incidence to sine of angle of refraction is constant for a given pair of media.
The twinkling of stars is due to atmospheric reflection.
Which of the following is Snell 's law.
How does the light should enter the glass to produce a large amount of bending?
During the refraction of light, the frequency of light remains constant.
If a ray of light passes obliquely from one medium to another, it does not suffer any deviation.
Speed of light in vacuum is _____ .
The speed of light is maximum in
